Alpha-ketoglutarate ameliorates age-related osteoporosis via regulating histone methylations
- PMID: 33154378
- PMCID: PMC7645772
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19360-1
Alpha-ketoglutarate ameliorates age-related osteoporosis via regulating histone methylations
Abstract
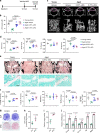
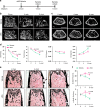
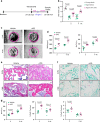
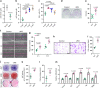
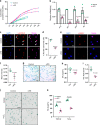
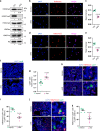
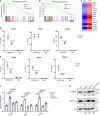
Age-related osteoporosis is characterized by the deterioration in bone volume and strength, partly due to the dysfunction of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) during aging. Alpha-ketoglutarate (αKG) is an essential intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Studies have revealed that αKG extends the lifespan of worms and maintains the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Here, we show that the administration of αKG increases the bone mass of aged mice, attenuates age-related bone loss, and accelerates bone regeneration of aged rodents. αKG ameliorates the senescence-associated (SA) phenotypes of bone marrow MSCs derived from aged mice, as well as promoting their proliferation, colony formation, migration, and osteogenic potential. Mechanistically, αKG decreases the accumulations of H3K9me3 and H3K27me3, and subsequently upregulates BMP signaling and Nanog expression. Collectively, our findings illuminate the role of αKG in rejuvenating MSCs and ameliorating age-related osteoporosis, with a promising therapeutic potential in age-related diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol counteracts bone loss via mitofilin-mediated osteogenic improvement of mesenchymal stem cells in senescence-accelerated mice.Theranostics. 2018 Mar 23;8(9):2387-2406. doi: 10.7150/thno.23620. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29721087 Free PMC article.
-
Low concentration flufenamic acid enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and suppresses bone loss by inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jul 19;10(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1321-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31324207 Free PMC article.
-
KDM5A controls bone morphogenic protein 2-induced osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells during osteoporosis.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Aug 11;7(8):e2335. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.238. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27512956 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoporosis: Emerging targets on the classical signaling pathways of bone formation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 15;973:176574. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176574. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38642670 Review.
-
Basic biology of skeletal aging: role of stress response pathways.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013 Oct;68(10):1197-208. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt079. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23825036 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy-Potential Implications in the Treatment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 29;17(10):1297. doi: 10.3390/ph17101297. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of Hyperglycemia on Epigenetic Modifications in Human Gingival Fibroblasts and Gingiva in Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 12;25(20):10979. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010979. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456763 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-aging Metabolite-Based Polymeric Microparticles for Intracellular Drug Delivery and Bone Regeneration.Small Sci. 2024 Oct 6;4(10):2400201. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400201. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 39386061
-
α-ketoglutarate produced by lactic acid bacteria inhibits hyaluronidase activity.Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2024;43(4):391-400. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2024-017. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2024. PMID: 39364123 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of chromatin and genome instability in cellular senescence and their relevance to ageing and related diseases.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Oct 3. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00775-3. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39363000 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

