Protective Effects of Flavonoids in Acute Models of Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration
- PMID: 33154094
- PMCID: PMC7736834
- DOI: 10.1124/molpharm.120.000072
Protective Effects of Flavonoids in Acute Models of Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration
Abstract
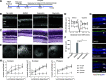
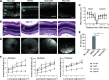
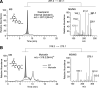
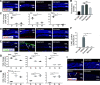
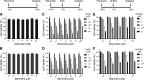
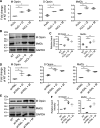
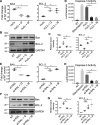
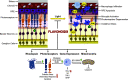
Degeneration of photoreceptors caused by excessive illumination, inherited mutations, or aging is the principal pathology of blinding diseases. Pharmacological compounds that stabilize the visual receptor rhodopsin and modulate the cellular pathways triggering death of photoreceptors could avert this pathology. Interestingly, flavonoids can modulate the cellular processes, such as oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and apoptosis, that are activated during retinal degeneration. As we found previously, flavonoids also bind directly to unliganded rod opsin, enhancing its folding, stability, and regeneration. In addition, flavonoids stimulate rhodopsin gene expression. Thus, we evaluated the effect of two main dietary flavonoids, quercetin and myricetin, in ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 4 -/- /retinol dehydrogenase 8 -/- and wild-type BALB/c mice susceptible to light-induced photoreceptor degeneration. Using in vivo imaging, such as optical coherence tomography, scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, and histologic assessment of retinal morphology, we found that treatment with these flavonoids prior to light insult remarkably protected retina from deterioration and preserved its function. Using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, we detected these flavonoids in the eye upon their intraperitoneal administration. The molecular events associated with the protective effect of quercetin and myricetin were related to the elevated expression of photoreceptor-specific proteins, rhodopsin and cone opsins, decreased expression of the specific inflammatory markers, and the shift of the equilibrium between cell death regulators BCL2-associated X protein (BAX) and B-cell lymphoma 2 toward an antiapoptotic profile. These results were confirmed in photoreceptor-derived 661W cells treated with either H2O2 or all-trans-retinal stressors implicated in the mechanism of retinal degeneration. Altogether, flavonoids could have significant prophylactic value for retinal degenerative diseases. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Flavonoids commonly present in food exhibit advantageous effects in blinding diseases. They bind to and stabilize unliganded rod opsin, which in excess accelerates degenerative processes in the retina. Additionally, flavonoids enhance the expression of the visual receptors, rod and cone opsins; inhibit the inflammatory reactions; and induce the expression of antiapoptotic markers in the retina, preventing the degeneration in vivo. Thus, flavonoids could have a prophylactic value for retinal degenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2020 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective Effect of a Locked Retinal Chromophore Analog against Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration.Mol Pharmacol. 2018 Oct;94(4):1132-1144. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.112581. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30018116 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine protects against light-induced photoreceptor degeneration in the mouse retina.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Apr;145:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26475979 Free PMC article.
-
Intraperitoneal chromophore injections delay early-onset and rapid retinal cone degeneration in a mouse model of Leber congenital amaurosis.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Nov;212:108776. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108776. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34582935
-
Polyphenols and Visual Health: Potential Effects on Degenerative Retinal Diseases.Molecules. 2021 Jun 4;26(11):3407. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113407. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34199888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neuroprotective Role of Retbindin, a Metabolic Regulator in the Neural Retina.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 6;13:919667. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919667. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rhodopsin as a Molecular Target to Mitigate Retinitis Pigmentosa.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1371:61-77. doi: 10.1007/5584_2021_682. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 34962636 Review.
-
Effect of palmitoylethanolamide on degeneration of a human-derived retinal pigment epithelial cell induced by all-trans retinal.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Feb 18;16(2):191-200. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.02.04. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36816211 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel cytoprotective small compounds inhibiting mitochondria-dependent cell death.iScience. 2023 Sep 17;26(10):107916. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107916. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37841588 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Epicatechin Provides Neuroprotection in Sodium Iodate-Induced Retinal Degeneration.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 27;9:879901. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.879901. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35833100 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin: A Bioactive Compound Imparting Cardiovascular and Neuroprotective Benefits: Scope for Exploring Fresh Produce, Their Wastes, and By-Products.Biology (Basel). 2021 Jun 26;10(7):586. doi: 10.3390/biology10070586. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bian M, Zhang Y, Du X, Xu J, Cui J, Gu J, Zhu W, Zhang T, Chen Y. (2017) Apigenin-7-diglucuronide protects retinas against bright light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through the inhibition of retinal oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res 1663:141–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
