Selecting a Scale for Spatial Confounding Adjustment
- PMID: 33132544
- PMCID: PMC7592711
- DOI: 10.1111/rssa.12556
Selecting a Scale for Spatial Confounding Adjustment
Abstract
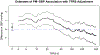
Unmeasured, spatially-structured factors can confound associations between spatial environmental exposures and health outcomes. Adding flexible splines to a regression model is a simple approach for spatial confounding adjustment, but the spline degrees of freedom do not provide an easily interpretable spatial scale. We describe a method for quantifying the extent of spatial confounding adjustment in terms of the Euclidean distance at which variation is removed. We develop this approach for confounding adjustment with splines and using Fourier and wavelet filtering. We demonstrate differences in the spatial scales these bases can represent and provide a comparison of methods for selecting the amount of confounding adjustment. We find the best performance for selecting the amount of adjustment using an information criterion evaluated on an outcome model without exposure. We apply this method to spatial adjustment in an analysis of fine particulate matter and blood pressure in a cohort of United States women.
Keywords: Air Pollution Epidemiology; Confounding; Regression Splines; Spatial Filtering.
Figures
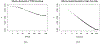



Similar articles
-
Extended follow-up and spatial analysis of the American Cancer Society study linking particulate air pollution and mortality.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2009 May;(140):5-114; discussion 115-36. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2009. PMID: 19627030
-
The importance of scale for spatial-confounding bias and precision of spatial regression estimators.Stat Sci. 2010 Feb;25(1):107-125. doi: 10.1214/10-STS326. Stat Sci. 2010. PMID: 21528104 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and statistical modeling of the relationship between remotely sensed aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 in the eastern United States.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012 May;(167):5-83; discussion 85-91. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012. PMID: 22838153
-
Air Pollution and Autism Spectrum Disorders: Causal or Confounded?Curr Environ Health Rep. 2015 Dec;2(4):430-9. doi: 10.1007/s40572-015-0073-9. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2015. PMID: 26399256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addressing unmeasured confounding in comparative observational research.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2018 Apr;27(4):373-382. doi: 10.1002/pds.4394. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2018. PMID: 29383840 Review.
Cited by
-
spconfShiny: An R Shiny application for calculating the spatial scale of smoothing splines for point data.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 4;19(10):e0311440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311440. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39365774 Free PMC article.
-
Source-Specific Air Pollution and Loss of Independence in Older Adults Across the US.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jun 3;7(6):e2418460. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.18460. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38941096 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral adjustment for spatial confounding.Biometrika. 2023 Sep;110(3):699-719. doi: 10.1093/biomet/asac069. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Biometrika. 2023. PMID: 38500847 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Air Pollution Exposures and Health Effects Associations Using 11 Different Modeling Approaches in the Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS).Environ Health Perspect. 2024 Jan;132(1):17003. doi: 10.1289/EHP12995. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Environ Health Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38226465 Free PMC article.
-
Residential Structural Racism and Prevalence of Chronic Health Conditions.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Dec 1;6(12):e2348914. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.48914. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 38127347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike H (1973). Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle In Petrov B and Csaki F (Eds.), Second International Symposium on Information Theory, pp. 267–281. Budapest: Akademiai Kiado.
-
- Besag J, York J, and Mollié A (1991). Bayesian image restoration with two applications in spatial statistics. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics 43(1), 1–20.
-
- Burger W and Burge JM (2009). Principles of Digital Image Processing: Core Algorithms. London: Springer.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
