Combating acquired resistance to MAPK inhibitors in melanoma by targeting Abl1/2-mediated reactivation of MEK/ERK/MYC signaling
- PMID: 33122628
- PMCID: PMC7596241
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19075-3
Combating acquired resistance to MAPK inhibitors in melanoma by targeting Abl1/2-mediated reactivation of MEK/ERK/MYC signaling
Abstract
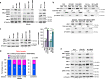
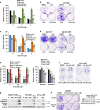
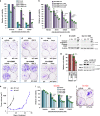
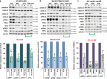
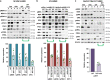
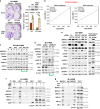
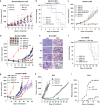
Metastatic melanoma remains an incurable disease for many patients due to the limited success of targeted and immunotherapies. BRAF and MEK inhibitors reduce metastatic burden for patients with melanomas harboring BRAF mutations; however, most eventually relapse due to acquired resistance. Here, we demonstrate that ABL1/2 kinase activities and/or expression are potentiated in cell lines and patient samples following resistance, and ABL1/2 drive BRAF and BRAF/MEK inhibitor resistance by inducing reactivation of MEK/ERK/MYC signaling. Silencing/inhibiting ABL1/2 blocks pathway reactivation, and resensitizes resistant cells to BRAF/MEK inhibitors, whereas expression of constitutively active ABL1/2 is sufficient to promote resistance. Significantly, nilotinib (2nd generation ABL1/2 inhibitor) reverses resistance, in vivo, causing prolonged regression of resistant tumors, and also, prevents BRAFi/MEKi resistance from developing in the first place. These data indicate that repurposing the FDA-approved leukemia drug, nilotinib, may be effective for prolonging survival for patients harboring BRAF-mutant melanomas.
Conflict of interest statement
This research is/was funded by the following grants to R.P.: National Institute of Health (NCI): R01 CA211137 and R01 CA166499; Lloyd Charitable Trust; University of Kentucky Markey Foundation Women’s Strong Award; and Cancer Center Support Grant Pilot Award (5P30CA177558). M.N. and A.R. are employees of Plexxikon Inc.; all other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas.Nature. 2017 Oct 5;550(7674):133-136. doi: 10.1038/nature24040. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28953887 Free PMC article.
-
ER Translocation of the MAPK Pathway Drives Therapy Resistance in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma.Cancer Discov. 2019 Mar;9(3):396-415. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0348. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30563872 Free PMC article.
-
Abl kinase regulation by BRAF/ERK and cooperation with Akt in melanoma.Oncogene. 2017 Aug 10;36(32):4585-4596. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.76. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28368422 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Development of BRAF plus MEK Inhibitor Combinations.Trends Cancer. 2020 Sep;6(9):797-810. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.05.009. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32540454 Review.
-
Targeting RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling in metastatic melanoma.IUBMB Life. 2013 Sep;65(9):748-58. doi: 10.1002/iub.1193. Epub 2013 Jul 29. IUBMB Life. 2013. PMID: 23893853 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profile of mitogen-activated kinases and microRNAs controlling their expression in HaCaT cell culture treated with lipopolysaccharide A and cyclosporine A.Cell Cycle. 2024 Feb;23(3):279-293. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2320508. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Cell Cycle. 2024. PMID: 38445655 Free PMC article.
-
MACC1 revisited - an in-depth review of a master of metastasis.Biomark Res. 2024 Nov 23;12(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00689-4. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39580452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MAP2K2 Gene as Potential Diagnostic Marker in Monitoring Adalimumab Therapy of Psoriatic Arthritis.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(2):330-340. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220628111644. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35762548
-
Supramolecular nanofibers co-loaded with dabrafenib and doxorubicin for targeted and synergistic therapy of differentiated thyroid carcinoma.Theranostics. 2023 Apr 1;13(7):2140-2153. doi: 10.7150/thno.82140. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37153748 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a miRNA-based non-invasive predictive biomarker of response to target therapy in BRAF-mutant melanoma.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 24;12(17):7420-7430. doi: 10.7150/thno.77761. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spagnolo, F., Boutros, A., Tanda, E. & Queirolo, P. The adjuvant treatment revolution for high-risk melanoma patients. Semin. Cancer Biol. 59, 283–289 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

