Animal Cell Cytokinesis: The Rho-Dependent Actomyosin-Anilloseptin Contractile Ring as a Membrane Microdomain Gathering, Compressing, and Sorting Machine
- PMID: 33117802
- PMCID: PMC7575755
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.575226
Animal Cell Cytokinesis: The Rho-Dependent Actomyosin-Anilloseptin Contractile Ring as a Membrane Microdomain Gathering, Compressing, and Sorting Machine
Abstract
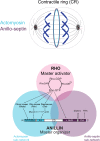
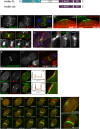
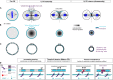
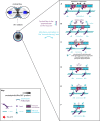
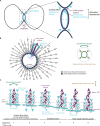
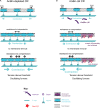
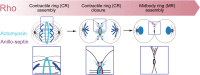
Cytokinesis is the last step of cell division that partitions the cellular organelles and cytoplasm of one cell into two. In animal cells, cytokinesis requires Rho-GTPase-dependent assembly of F-actin and myosin II (actomyosin) to form an equatorial contractile ring (CR) that bisects the cell. Despite 50 years of research, the precise mechanisms of CR assembly, tension generation and closure remain elusive. This hypothesis article considers a holistic view of the CR that, in addition to actomyosin, includes another Rho-dependent cytoskeletal sub-network containing the scaffold protein, Anillin, and septin filaments (collectively termed anillo-septin). We synthesize evidence from our prior work in Drosophila S2 cells that actomyosin and anillo-septin form separable networks that are independently anchored to the plasma membrane. This latter realization leads to a simple conceptual model in which CR assembly and closure depend upon the micro-management of the membrane microdomains to which actomyosin and anillo-septin sub-networks are attached. During CR assembly, actomyosin contractility gathers and compresses its underlying membrane microdomain attachment sites. These microdomains resist this compression, which builds tension. During CR closure, membrane microdomains are transferred from the actomyosin sub-network to the anillo-septin sub-network, with which they flow out of the CR as it advances. This relative outflow of membrane microdomains regulates tension, reduces the circumference of the CR and promotes actomyosin disassembly all at the same time. According to this hypothesis, the metazoan CR can be viewed as a membrane microdomain gathering, compressing and sorting machine that intrinsically buffers its own tension through coordination of actomyosin contractility and anillo-septin-membrane relative outflow, all controlled by Rho. Central to this model is the abandonment of the dogmatic view that the plasma membrane is always readily deformable by the underlying cytoskeleton. Rather, the membrane resists compression to build tension. The notion that the CR might generate tension through resistance to compression of its own membrane microdomain attachment sites, can account for numerous otherwise puzzling observations and warrants further investigation using multiple systems and methods.
Keywords: anillin; contractile ring mechanism; contractile ring tension; cytokinesis; membrane cytoskeleton; membrane microdomains; rho (Rho GTPase); septin.
Copyright © 2020 Carim, Kechad and Hickson.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Rho1 GTPase controls anillo-septin assembly to facilitate contractile ring closure during cytokinesis.iScience. 2023 May 19;26(6):106903. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106903. eCollection 2023 Jun 16. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37378349 Free PMC article.
-
Building the cytokinetic contractile ring in an early embryo: Initiation as clusters of myosin II, anillin and septin, and visualization of a septin filament network.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 28;16(12):e0252845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252845. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34962917 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of Contractile Ring Tension Using Two-photon Laser Ablation during Drosophila Cellularization.Bio Protoc. 2022 Mar 20;12(6):e4362. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4362. eCollection 2022 Mar 20. Bio Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35434185 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and Assembly of Actomyosin Contractile Rings in Cytokinesis and Cell Repair.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2018 Dec;301(12):2051-2066. doi: 10.1002/ar.23962. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 30312008 Review.
-
How to scaffold the contractile ring for a safe cytokinesis - lessons from Anillin-related proteins.J Cell Sci. 2009 Apr 15;122(Pt 8):1071-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.034785. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19339546 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Methods to Monitor Cardiomyocyte Proliferation.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Mar 3;9(3):73. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9030073. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 35323621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity is the spice of life: An overview of how cytokinesis regulation varies with cell type.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 7;10:1007614. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1007614. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36420142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokinetic contractile ring structural progression in an early embryo: positioning of scaffolding proteins, recruitment of α-actinin, and effects of myosin II inhibition.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Sep 27;12:1483345. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1483345. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39398481 Free PMC article.
-
Septins regulate border cell surface geometry, shape, and motility downstream of Rho in Drosophila.Dev Cell. 2023 Aug 7;58(15):1399-1413.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.05.017. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Dev Cell. 2023. PMID: 37329886 Free PMC article.
-
Anillin forms linear structures and facilitates furrow ingression after septin and formin depletion.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113076. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113076. Epub 2023 Sep 3. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37665665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe M., Makino A., Hullin-Matsuda F., Kamijo K., Ohno-Iwashita Y., Hanada K., et al. (2012). A role for sphingomyelin-rich lipid domains in the accumulation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate to the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 32 1396–1407. 10.1128/mcb.06113-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

