Dracocephalum heterophyllum (DH) Exhibits Potent Anti-Proliferative Effects on Autoreactive CD4+ T Cells and Ameliorates the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
- PMID: 33117376
- PMCID: PMC7578250
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.575669
Dracocephalum heterophyllum (DH) Exhibits Potent Anti-Proliferative Effects on Autoreactive CD4+ T Cells and Ameliorates the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
Abstract
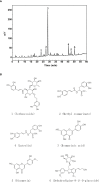
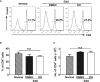
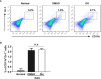
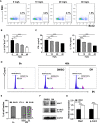
Experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) is a CD4+ T cell-mediated organ-specific autoimmune disease and has been considered as a model of human autoimmune uveitis. Dracocephalum heterophyllum (DH) is a Chinese herbal medicine used in treating hepatitis. DH suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines through the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) to the liver. However, it remains elusive whether DH can directly regulate CD4+ T cell biology and hence ameliorates the development of CD4+ T cell-mediated autoimmune disease. In the current study, we found that DH extract significantly suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by CD4+ T cells. Further study showed that DH didn't affect the activation, differentiation, and apoptosis of CD4+ T cells. Instead, it significantly suppressed the proliferation of conventional CD4+ T cells both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistic study showed that DH-treated CD4+ T cells were partially arrested at the G2/M phase of the cell cycle because of the enhanced inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdc2 (Tyr15). In addition, we demonstrated that treatment with DH significantly ameliorated EAU in mice through suppressing the proliferation of autoreactive antigen specific CD4+ T cells. Taken together, the current study indicates that DH-mediated suppression of CD4+ T cell proliferation may provide a promising therapeutic strategy for treating CD4+ T cell-mediated diseases.
Keywords: T cell; autoimmunity; experimental autoimmune uveitis; herbal medicine; proliferation.
Copyright © 2020 Bian, Wang, Wang, Wang, Wang, Shi and Ruan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longdan Xiegan Decoction alleviates experimental autoimmune uveitis in rats by inhibiting Notch signaling pathway activation and Th17 cell differentiation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Apr;136:111291. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111291. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33493870
-
Immunomodulatory effects of Longdan Xiegan Tang on CD4+/CD8+ T cells and associated inflammatory cytokines in rats with experimental autoimmune uveitis.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):2746-54. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5558. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27485320
-
A20 Inhibits Intraocular Inflammation in Mice by Regulating the Function of CD4+T Cells and RPE Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 4;11:603939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.603939. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33613524 Free PMC article.
-
Uveitis: Molecular Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 30;12:623725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.623725. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What causes relapses of autoimmune diseases? The etiological role of autoreactive T cells.Autoimmun Rev. 2013 Sep;12(11):1070-5. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 May 16. Autoimmun Rev. 2013. PMID: 23685277 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-21 Regulates Diametrically Opposed Biological Functions of Regulatory T Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 11;12:766757. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.766757. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858422 Free PMC article.
-
The Isolation and Preparation of Samwinol from Dracocephalum heterophyllum and Prevention on Aβ25-35-Induced Neuroinflammation in PC-12 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 30;23(19):11572. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911572. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232874 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical, and Pharmacological Properties of the Subfamily Nepetoideae (Lamiaceae) in Inflammatory Diseases.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;12(21):3752. doi: 10.3390/plants12213752. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caspi RR, Roberge FG, Chan CC, Wiggert B, Chader GJ, Rozenszajn LA, et al. A new model of autoimmune disease. Experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis induced in mice with two different retinal antigens. J Immunol (1988) 140:1490–5. - PubMed
-
- Tarrant TK, Silver PB, Wahlsten JL, Rizzo LV, Chan CC, Wiggert B, et al. Interleukin 12 protects from a T helper type 1-mediated autoimmune disease, experimental autoimmune uveitis, through a mechanism involving interferon gamma, nitric oxide, and apoptosis. J Exp Med (1999) 189:219–30. 10.1084/jem.189.2.219 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

