K-Ras-Activated Cells Can Develop into Lung Tumors When Runx3-Mediated Tumor Suppressor Pathways Are Abrogated
- PMID: 33115981
- PMCID: PMC7604022
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2020.0182
K-Ras-Activated Cells Can Develop into Lung Tumors When Runx3-Mediated Tumor Suppressor Pathways Are Abrogated
Abstract
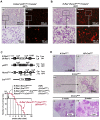
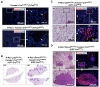
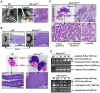
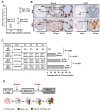
K-RAS is frequently mutated in human lung adenocarcinomas (ADCs), and the p53 pathway plays a central role in cellular defense against oncogenic K-RAS mutation. However, in mouse lung cancer models, oncogenic K-RAS mutation alone can induce ADCs without p53 mutation, and loss of p53 does not have a significant impact on early K-RAS-induced lung tumorigenesis. These results raise the question of how K-RAS-activated cells evade oncogene surveillance mechanisms and develop into lung ADCs. RUNX3 plays a key role at the restriction (R)-point, which governs multiple tumor suppressor pathways including the p14ARF-p53 pathway. In this study, we found that K-RAS activation in a very limited number of cells, alone or in combination with p53 inactivation, failed to induce any pathologic lesions for up to 1 year. By contrast, when Runx3 was inactivated and K-RAS was activated by the same targeting method, lung ADCs and other tumors were rapidly induced. In a urethane-induced mouse lung tumor model that recapitulates the features of K-RAS-driven human lung tumors, Runx3 was inactivated in both adenomas (ADs) and ADCs, whereas K-RAS was activated only in ADCs. Together, these results demonstrate that the R-point-associated oncogene surveillance mechanism is abrogated by Runx3 inactivation in AD cells and these cells cannot defend against K-RAS activation, resulting in the transition from AD to ADC. Therefore, K-RAS-activated lung epithelial cells do not evade oncogene surveillance mechanisms; instead, they are selected if they occur in AD cells in which Runx3 has been inactivated.
Keywords: K-Ras; Runx3; cancer initiation; lung cancer; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Runx3 Restoration Regresses K-Ras-Activated Mouse Lung Cancers and Inhibits Recurrence.Cells. 2023 Oct 11;12(20):2438. doi: 10.3390/cells12202438. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887282 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RUNX3 in Restriction Point Regulation.Cells. 2023 Feb 23;12(5):708. doi: 10.3390/cells12050708. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Runx3 inactivation is a crucial early event in the development of lung adenocarcinoma.Cancer Cell. 2013 Nov 11;24(5):603-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.10.003. Cancer Cell. 2013. PMID: 24229708
-
Runx3 is required for the differentiation of lung epithelial cells and suppression of lung cancer.Oncogene. 2010 Jun 10;29(23):3349-61. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.79. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20228843
-
How do K-RAS-activated cells evade cellular defense mechanisms?Oncogene. 2016 Feb 18;35(7):827-32. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.153. Epub 2015 May 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25961920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Runx3 Restoration Regresses K-Ras-Activated Mouse Lung Cancers and Inhibits Recurrence.Cells. 2023 Oct 11;12(20):2438. doi: 10.3390/cells12202438. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887282 Free PMC article.
-
From targeted therapy to a novel way: Immunogenic cell death in lung cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 23;9:1102550. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1102550. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36619616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TGFβ→TAK1→LATS→YAP1 Pathway Regulates the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of YAP1.Mol Cells. 2023 Oct 31;46(10):592-610. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.0088. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 37706312 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RUNX3 in Restriction Point Regulation.Cells. 2023 Feb 23;12(5):708. doi: 10.3390/cells12050708. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

