The Role of Sumoylation in the Response to Hypoxia: An Overview
- PMID: 33114748
- PMCID: PMC7693722
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9112359
The Role of Sumoylation in the Response to Hypoxia: An Overview
Abstract
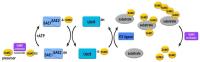
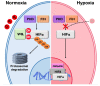
Sumoylation is the covalent attachment of the small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) to a vast variety of proteins in order to modulate their function. Sumoylation has emerged as an important modification with a regulatory role in the cellular response to different types of stress including osmotic, hypoxic and oxidative stress. Hypoxia can occur under physiological or pathological conditions, such as ischemia and cancer, as a result of an oxygen imbalance caused by low supply and/or increased consumption. The hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs), and the proteins that regulate their fate, are critical molecular mediators of the response to hypoxia and modulate procedures such as glucose and lipid metabolism, angiogenesis, erythropoiesis and, in the case of cancer, tumor progression and metastasis. Here, we provide an overview of the sumoylation-dependent mechanisms that are activated under hypoxia and the way they influence key players of the hypoxic response pathway. As hypoxia is a hallmark of many diseases, understanding the interrelated connections between the SUMO and the hypoxic signaling pathways can open the way for future molecular therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: HIF; HIF-1α; SUMO; hypoxia; oxygen homeostasis; sumoylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-induced Changes in SUMO Conjugation Affect Transcriptional Regulation Under Low Oxygen.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Jun;18(6):1197-1209. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001401. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30926672 Free PMC article.
-
Global SUMOylation facilitates the multimodal neuroprotection afforded by quercetin against the deleterious effects of oxygen/glucose deprivation and the restoration of oxygen/glucose.J Neurochem. 2016 Jul;138(1):101-16. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13643. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27087120 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation indirectly suppresses activity of the HIF-1α pathway in intestinal epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2023 Nov;299(11):105280. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105280. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37742924 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO under stress.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Oct;36(Pt 5):874-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0360874. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18793154 Review.
-
The Roles of SUMO in Metabolic Regulation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:143-168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Potential of Exosomal HypoxamiRs in the Context of Hypoxia-Sumoylation-HypoxamiRs in Early Onset Preeclampsia at the Preclinical Stage.Life (Basel). 2022 Jan 11;12(1):101. doi: 10.3390/life12010101. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054494 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation and NEDDylation in Primary and Metastatic Cancers to Bone.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 6;10:889002. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.889002. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35465332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF-1-Independent Mechanisms Regulating Metabolic Adaptation in Hypoxic Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2371. doi: 10.3390/cells10092371. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Mitochondria: An Intimate Connection.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 27;13(1):50. doi: 10.3390/biom13010050. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36671435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUMOtherapeutics for Ischemic Stroke.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;16(5):673. doi: 10.3390/ph16050673. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

