Gradual compaction of the nascent peptide during cotranslational folding on the ribosome
- PMID: 33112737
- PMCID: PMC7593090
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60895
Gradual compaction of the nascent peptide during cotranslational folding on the ribosome
Abstract
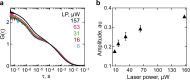
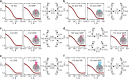
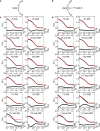
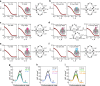
Nascent polypeptides begin to fold in the constrained space of the ribosomal peptide exit tunnel. Here we use force-profile analysis (FPA) and photo-induced energy-transfer fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (PET-FCS) to show how a small α-helical domain, the N-terminal domain of HemK, folds cotranslationally. Compaction starts vectorially as soon as the first α-helical segments are synthesized. As nascent chain grows, emerging helical segments dock onto each other and continue to rearrange at the vicinity of the ribosome. Inside or in the proximity of the ribosome, the nascent peptide undergoes structural fluctuations on the µs time scale. The fluctuations slow down as the domain moves away from the ribosome. Mutations that destabilize the packing of the domain's hydrophobic core have little effect on folding within the exit tunnel, but abolish the final domain stabilization. The results show the power of FPA and PET-FCS in solving the trajectory of cotranslational protein folding and in characterizing the dynamic properties of folding intermediates.
Keywords: HemK; PET-FCS; biochemistry; chemical biology; cotranslational folding; nascent chain dynamics; ribosome.
© 2020, Liutkute et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ML, MM, ES, JE, MR No competing interests declared
Figures
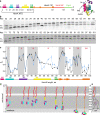
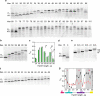
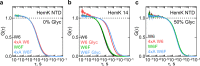
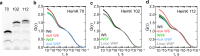

Similar articles
-
Cotranslational protein folding on the ribosome monitored in real time.Science. 2015 Nov 27;350(6264):1104-7. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0344. Science. 2015. PMID: 26612953
-
Force-Profile Analysis of the Cotranslational Folding of HemK and Filamin Domains: Comparison of Biochemical and Biophysical Folding Assays.J Mol Biol. 2019 Mar 15;431(6):1308-1314. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.043. Epub 2019 Feb 7. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30738895
-
How the ribosome shapes cotranslational protein folding.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Feb;84:102740. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102740. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38071940 Review.
-
Co-Translational Folding Trajectory of the HemK Helical Domain.Biochemistry. 2018 Jun 26;57(25):3460-3464. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00293. Epub 2018 May 14. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29741886
-
Cotranslational Folding of Proteins on the Ribosome.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 7;10(1):97. doi: 10.3390/biom10010097. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31936054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Geometric differences in the ribosome exit tunnel impact the escape of small nascent proteins.Biophys J. 2023 Jan 3;122(1):20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.11.2945. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36463403 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient integration of transmembrane domains depends on the folding properties of the upstream sequences.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 17;118(33):e2102675118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2102675118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34373330 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between nascent proteins and the ribosome surface inhibit co-translational folding.Nat Chem. 2021 Dec;13(12):1214-1220. doi: 10.1038/s41557-021-00796-x. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Nat Chem. 2021. PMID: 34650236 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Evidence for a Helical Nascent Chain.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 26;11(3):357. doi: 10.3390/biom11030357. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33652806 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence Anisotropy Decays and Microscale-Volume Viscometry Reveal the Compaction of Ribosome-Bound Nascent Proteins.J Phys Chem B. 2021 Jun 24;125(24):6543-6558. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c04473. Epub 2021 Jun 10. J Phys Chem B. 2021. PMID: 34110829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhushan S, Gartmann M, Halic M, Armache JP, Jarasch A, Mielke T, Berninghausen O, Wilson DN, Beckmann R. alpha-Helical nascent polypeptide chains visualized within distinct regions of the ribosomal exit tunnel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2010;17:313–317. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1756. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

