MIR448 antagomir reduces arrhythmic risk after myocardial infarction by upregulating the cardiac sodium channel
- PMID: 33108349
- PMCID: PMC7714400
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.140759
MIR448 antagomir reduces arrhythmic risk after myocardial infarction by upregulating the cardiac sodium channel
Abstract
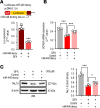
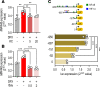
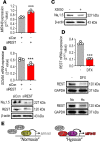
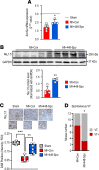
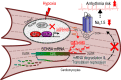
Cardiac ischemia is associated with arrhythmias; however, effective therapies are currently limited. The cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel α subunit (SCN5A), encoding the Nav1.5 current, plays a key role in the cardiac electrical conduction and arrhythmic risk. Here, we show that hypoxia reduces Nav1.5 through effects on a miR, miR-448. miR-448 expression is increased in ischemic cardiomyopathy. miR-448 has a conserved binding site in 3'-UTR of SCN5A. miR-448 binding to this site suppressed SCN5A expression and sodium currents. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α and NF-κB were major transcriptional regulators for MIR448. Moreover, hypoxia relieved MIR448 transcriptional suppression by RE1 silencing transcription factor. Therefore, miR-448 inhibition reduced arrhythmic risk after myocardial infarction. Here, we show that ischemia drove miR-448 expression, reduced Nav1.5 current, and increased arrhythmic risk. Arrhythmic risk was improved by preventing Nav1.5 downregulation, suggesting a new approach to antiarrhythmic therapy.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; Cardiology; Sodium channels; hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 inhibited ischemic arrhythmias via targeting miR-143/EGR1 axis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2020 Jan 4;115(2):9. doi: 10.1007/s00395-019-0768-4. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31900593
-
HuR-mediated SCN5A messenger RNA stability reduces arrhythmic risk in heart failure.Heart Rhythm. 2018 Jul;15(7):1072-1080. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.02.018. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Heart Rhythm. 2018. PMID: 29454929 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of FoxO1 leads to shortening of QRS by increasing Na(+) channel activity through enhanced expression of both cardiac NaV1.5 and β3 subunit.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Sep;74:297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jun 21. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24956219 Free PMC article.
-
Heritable arrhythmia syndromes associated with abnormal cardiac sodium channel function: ionic and non-ionic mechanisms.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Jul 15;116(9):1557-1570. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa082. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 32251506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SCN5A channelopathy: arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, epilepsy and beyond.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;378(1879):20220164. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0164. Epub 2023 May 1. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37122208 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ranolazine: a potential anti-metastatic drug targeting voltage-gated sodium channels.Br J Cancer. 2024 May;130(9):1415-1419. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02622-w. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38424164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrophysiological Mechanisms Underlying T-Wave Alternans and Their Role in Arrhythmogenesis.Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 4;12:614946. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.614946. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33746768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia Leads to miRNA Alterations in Different Brain Regions, Blood Serum, Liver, and Spleen.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 23;23(1):161. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010161. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008586 Free PMC article.
-
miR-448 regulates potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 4 (KCNA4) in ischemia and heart failure.Heart Rhythm. 2023 May;20(5):730-736. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2023.01.021. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Heart Rhythm. 2023. PMID: 36693615 Free PMC article.
-
Multilayer control of cardiac electrophysiology by microRNAs.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 May;166:107-115. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.02.007. Epub 2022 Mar 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35247375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zaklyazminskaya E, Dzemeshkevich S. The role of mutations in the SCN5A gene in cardiomyopathies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863(7 Pt B):1799–1805. - PubMed
-
- Zumhagen S, et al. A heterozygous deletion mutation in the cardiac sodium channel gene SCN5A with loss- and gain-of-function characteristics manifests as isolated conduction disease, without signs of Brugada or long QT syndrome. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067963. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aromolaran AS, Chahine M, Boutjdir M. Regulation of cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel by kinases: roles of protein kinases A and C. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;246:161–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

