Development of a multiomics database for personalized prognostic forecasting in head and neck cancer: The Big Data to Decide EU Project
- PMID: 33107152
- PMCID: PMC7820974
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.26515
Development of a multiomics database for personalized prognostic forecasting in head and neck cancer: The Big Data to Decide EU Project
Abstract
Background: Despite advances in treatments, 30% to 50% of stage III-IV head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients relapse within 2 years after treatment. The Big Data to Decide (BD2Decide) project aimed to build a database for prognostic prediction modeling.
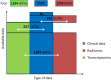
Methods: Stage III-IV HNSCC patients with locoregionally advanced HNSCC treated with curative intent (1537) were included. Whole transcriptomics and radiomics analyses were performed using pretreatment tumor samples and computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging scans, respectively.
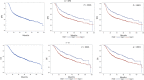
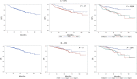
Results: The entire cohort was composed of 71% male (1097)and 29% female (440): oral cavity (429, 28%), oropharynx (624, 41%), larynx (314, 20%), and hypopharynx (170, 11%); median follow-up 50.5 months. Transcriptomics and imaging data were available for 1284 (83%) and 1239 (80%) cases, respectively; 1047 (68%) patients shared both.
Conclusions: This annotated database represents the HNSCC largest available repository and will enable to develop/validate a decision support system integrating multiscale data to explore through classical and machine learning models their prognostic role.
Keywords: big data; head and neck cancer; prognostic models; radiomics; transcriptomics.
© 2020 The Authors. Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Yes Author Lisa Licitra has disclosed funding (to her institution) for clinical studies and research from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, and Roche, has received compensation for service as a consultant/advisor and/or for lectures from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Debiopharm, Eisai, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Roche, and Sobi; and has received travel coverage for meetings from Bayer, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Debiopharm, Merck Serono, MSD, and Sobi. Author Ron Shefi (and the additional person Avner Algom, acknowledged within the “BD2Decide Consortium”) is employed by the company All‐In‐Image Ltd, Israel. Author Vasilis Tountopoulos (and the additional person Thanasis Dalianis, acknowledged within the “BD2Decide Consortium”) is employed by the company Technical Implementation, Innovation Lab, Athens Technology Center, Greece. Author Franco Mercalli (and the additional person Sergio Copelli, acknowledged within the “BD2Decide Consortium”) is employed by the company MultiMed Engineers, Parma, Italy. Stefan Wesarg, acknowledged within the “BD2Decide Consortium”, is employed by the company Fraunhofer, Munich, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computed tomography-derived radiomic signature of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (peri)tumoral tissue for the prediction of locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis after concurrent chemo-radiotherapy.PLoS One. 2020 May 22;15(5):e0232639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232639. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32442178 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome prediction of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by MRI radiomic signatures.Eur Radiol. 2020 Nov;30(11):6311-6321. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06962-y. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32500196 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment ADC is not a prognostic factor for local recurrences in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma when clinical T-stage is known.Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):1228-1231. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06426-y. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31529258 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics and radiogenomics in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Potential contribution to patient management and challenges.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Sep;99:102263. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102263. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34343892 Review.
-
Big Data in Head and Neck Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2018 Oct 25;19(12):62. doi: 10.1007/s11864-018-0585-2. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30361937 Review.
Cited by
-
A multicenter randomized trial for quality of life evaluation by non-invasive intelligent tools during post-curative treatment follow-up for head and neck cancer: Clinical study protocol.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 31;13:1048593. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1048593. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36798825 Free PMC article.
-
An MRI-based radiomics-clinical nomogram for the overall survival prediction in patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: a multi-cohort study.Eur Radiol. 2022 Mar;32(3):1548-1557. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08292-z. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34665315
-
Developing a robust two-step machine learning multiclassification pipeline to predict primary site in head and neck carcinoma from lymph nodes.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 12;10(2):e24377. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24377. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312621 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Management: A State-of-the-Art Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 6;11(3):805. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030805. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Prospectively Validated Prognostic Model for Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Based on Radiomics of Computed Tomography Images.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;13(13):3271. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133271. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34210048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sobin LH, MK WC Gospodarowicz. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 7th ed Oxford: Wiley‐Blackwell; 2010:349–445. doi:10.1016/B978-1-4377-0272-9.50014-0 - DOI

