Genetic markers and phosphoprotein forms of beta-catenin pβ-Cat552 and pβ-Cat675 are prognostic biomarkers of cervical cancer
- PMID: 33096476
- PMCID: PMC7581879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103049
Genetic markers and phosphoprotein forms of beta-catenin pβ-Cat552 and pβ-Cat675 are prognostic biomarkers of cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer (CC) remains a leading cause of gynaecological cancer-related mortality world wide and constitutes the third most common malignancy in women. The RAIDs consortium (http://www.raids-fp7.eu/) conducted a prospective European study [BioRAIDs (NCT02428842)] with the objective to stratify CC patients for innovative treatments. A "metagene" of genomic markers in the PI3K pathway and epigenetic regulators had been previously associated with poor outcome [2].
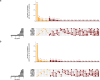
Methods: To detect new, more specific, targets for treatment of patients who resist standard chemo-radiation, a high-dimensional Cox model was applied to define dominant molecular variants, copy number variations, and reverse phase protein arrays (RPPA).
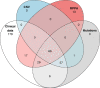
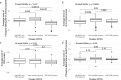
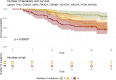
Findings: Survival analysis on 89 patients with all omics data available, suggested loss-of-function (LOF) or activating molecular alterations in nine genes to be candidate biomarkers for worse prognosis in patients treated by chemo-radiation while LOF of ATRX, MED13 as well as CASP8 were associated with better prognosis. When protein expression data by RPPA were factored in, the supposedly low molecular weight and nuclear form, of beta-catenin, phosphorylated in Ser552 (pβ-Cat552), ranked highest for good prognosis, while pβ-Cat675 was associated with worse prognosis.
Interpretation: These findings call for molecularly targeted treatments involving p53, Wnt pathway, PI3K pathway, and epigenetic regulator genes. Pβ-Cat552 and pβ-Cat675 may be useful biomarkers to predict outcome to chemo-radiation, which targets the DNA repair axis.
Funding: European Union's Seventh Program for research, technological development and demonstration (agreement N°304,810), the Fondation ARC pour la recherche contre le cancer.
Keywords: Beta-catenin pβ-cat552 and pβ-cat675; Cervical cancer; Molecular and protein biomarkers for chemo-radiation efficiency; Molecular landscape.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests All authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RAIDS atlas of significant genetic and protein biomarkers in cervical cancer.J Gynecol Oncol. 2023 Sep;34(5):e74. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2023.34.e74. J Gynecol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37668079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and genetic landscape of treatment naive cervical cancer: Alterations in PIK3CA and in epigenetic modulators associated with sub-optimal outcome.EBioMedicine. 2019 May;43:253-260. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.069. Epub 2019 Apr 2. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30952619 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localizaiton of β-catenin is associated with poor survival and chemo-/radioresistance in human cervical squamous cell cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jun 15;7(7):3908-17. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25120767 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM29 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway in cervical cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28579-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8686. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27081037 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic cell biological markers in cervical cancer patients primarily treated with (chemo)radiation: a systematic review.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Feb 1;79(2):325-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.09.043. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21195874 Review.
Cited by
-
ATRX is a predictive marker for endocrinotherapy and chemotherapy resistance in HER2-/HR+ breast cancer through the regulation of the AR, GLI3 and GATA2 transcriptional network.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Dec 20;15(24):14996-15024. doi: 10.18632/aging.205327. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 38126976 Free PMC article.
-
RAIDS atlas of significant genetic and protein biomarkers in cervical cancer.J Gynecol Oncol. 2023 Sep;34(5):e74. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2023.34.e74. J Gynecol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37668079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological Significance of ATRX Expression in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients: A Retrospective Study.J Cancer. 2021 Oct 3;12(23):6931-6936. doi: 10.7150/jca.63333. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34729095 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating HPV DNA as a Marker for Early Detection of Relapse in Patients with Cervical Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Nov 1;27(21):5869-5877. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0625. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34210686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Albert Einstein College of Medicine. Analytical Biological Services. Barretos Cancer Hospital. Baylor College of Medicine. Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope Integrated genomic and molecular characterization of cervical cancer. Nature. 2017;543(7645):378–384. 16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le Tourneau C., Delord J.-.P., Gonçalves A., Gavoille C., Dubot C., Isambert N. Molecularly targeted therapy based on tumour molecular profiling versus conventional therapy for advanced cancer (SHIVA): a multicentre, open-label, proof-of-concept, randomised, controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015 Oct;16(13):1324–1334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

