Dynamics of Vesicles Driven Into Closed Constrictions by Molecular Motors
- PMID: 33095297
- PMCID: PMC8646266
- DOI: 10.1007/s11538-020-00820-0
Dynamics of Vesicles Driven Into Closed Constrictions by Molecular Motors
Abstract
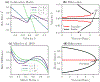
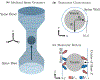
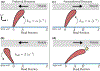
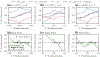
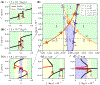
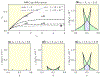
We study the dynamics of a model of membrane vesicle transport into dendritic spines, which are bulbous intracellular compartments in neurons driven by molecular motors. We reduce the lubrication model proposed in Fai et al. (Phys Rev Fluids 2:113601, 2017) to a fast-slow system, yielding an analytically and numerically tractable equation equivalent to the original model in the overdamped limit. The model's key parameters include: (1) the ratio of motors that prefer to push toward the head of the dendritic spine to the motors that prefer to push in the opposite direction, and (2) the viscous drag exerted on the vesicle by the spine constriction. We perform a numerical bifurcation analysis in these parameters and find that steady-state vesicle velocities appear and disappear through several saddle-node bifurcations. This process allows us to identify the region of parameter space in which multiple stable velocities exist. We show by direct calculations that there can only be unidirectional motion for sufficiently close vesicle-to-spine diameter ratios. Our analysis predicts the critical vesicle-to-spine diameter ratio, at which there is a transition from unidirectional to bidirectional motion, consistent with experimental observations of vesicle trajectories in the literature.
Keywords: Cell physiology; Dendritic spines; Motor transport; Neurophysiology; Vesicle transport.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
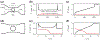
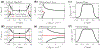
Similar articles
-
Coarse-grained Stochastic Model of Myosin-Driven Vesicles into Dendritic Spines.SIAM J Appl Math. 2022;82(3):793-820. doi: 10.1137/21m1434180. Epub 2022 May 12. SIAM J Appl Math. 2022. PMID: 36314039 Free PMC article.
-
Motor coordination via a tug-of-war mechanism drives bidirectional vesicle transport.Curr Biol. 2010 Apr 27;20(8):697-702. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.058. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20399099 Free PMC article.
-
Lattice-gas model for active vesicle transport by molecular motors with opposite polarities.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010 Aug;82(2 Pt 1):021925. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.82.021925. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010. PMID: 20866855
-
Myosin-V, a versatile motor for short-range vesicle transport.Traffic. 2002 Dec;3(12):859-65. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.31202.x. Traffic. 2002. PMID: 12453149 Review.
-
Physiopathologic dynamics of vesicle traffic in astrocytes.Histol Histopathol. 2011 Feb;26(2):277-84. doi: 10.14670/HH-26.277. Histol Histopathol. 2011. PMID: 21154240 Review.
Cited by
-
Coarse-grained Stochastic Model of Myosin-Driven Vesicles into Dendritic Spines.SIAM J Appl Math. 2022;82(3):793-820. doi: 10.1137/21m1434180. Epub 2022 May 12. SIAM J Appl Math. 2022. PMID: 36314039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acheson David J. Elementary fluid dynamics, 1991.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

