Common mechanistic pathways in cancer and heart failure. A scientific roadmap on behalf of the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)
- PMID: 33094495
- PMCID: PMC7894564
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.2029
Common mechanistic pathways in cancer and heart failure. A scientific roadmap on behalf of the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)
Abstract
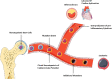
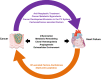
The co-occurrence of cancer and heart failure (HF) represents a significant clinical drawback as each disease interferes with the treatment of the other. In addition to shared risk factors, a growing body of experimental and clinical evidence reveals numerous commonalities in the biology underlying both pathologies. Inflammation emerges as a common hallmark for both diseases as it contributes to the initiation and progression of both HF and cancer. Under stress, malignant and cardiac cells change their metabolic preferences to survive, which makes these metabolic derangements a great basis to develop intersection strategies and therapies to combat both diseases. Furthermore, genetic predisposition and clonal haematopoiesis are common drivers for both conditions and they hold great clinical relevance in the context of personalized medicine. Additionally, altered angiogenesis is a common hallmark for failing hearts and tumours and represents a promising substrate to target in both diseases. Cardiac cells and malignant cells interact with their surrounding environment called stroma. This interaction mediates the progression of the two pathologies and understanding the structure and function of each stromal component may pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies and improved outcomes in patients. The interdisciplinary collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists is essential to establish unified guidelines. To this aim, pre-clinical models that mimic the human situation, where both pathologies coexist, are needed to understand all the aspects of the bidirectional relationship between cancer and HF. Finally, adequately powered clinical studies, including patients from all ages, and men and women, with proper adjudication of both cancer and cardiovascular endpoints, are essential to accurately study these two pathologies at the same time.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cancer; Cardio-oncology; Cardiotoxicity; Clonal haematopoiesis; Extracellular matrix; Heart failure; Inflammation; Metabolism.
© 2020 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of cardiovascular imaging in cancer patients receiving cardiotoxic therapies: a position statement on behalf of the Heart Failure Association (HFA), the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) and the Cardio-Oncology Council of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).Eur J Heart Fail. 2020 Sep;22(9):1504-1524. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1957. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 32621569
-
Recent advances in cardio-oncology: a report from the 'Heart Failure Association 2019 and World Congress on Acute Heart Failure 2019'.ESC Heart Fail. 2019 Dec;6(6):1140-1148. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12551. Epub 2019 Dec 28. ESC Heart Fail. 2019. PMID: 31884717 Free PMC article.
-
Cardio-oncological dialogue: Understanding the mechanistic correlation between heart failure and cancer.Life Sci. 2024 Dec 1;358:123170. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123170. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39490523 Review.
-
Inflammation: a common contributor to cancer, aging, and cardiovascular diseases-expanding the concept of cardio-oncology.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Apr 15;115(5):824-829. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz058. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30830168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New-Onset Cancer in the HF Population: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2021 Aug;18(4):191-199. doi: 10.1007/s11897-021-00517-y. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2021. PMID: 34181210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential: associations with heart failure incidence, clinical parameters and biomarkers.Eur J Heart Fail. 2023 Jan;25(1):4-13. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2715. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Eur J Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36221810 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving field of cardio-oncology.Cancer Pathog Ther. 2023 Feb 10;1(2):141-145. doi: 10.1016/j.cpt.2023.02.002. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cancer Pathog Ther. 2023. PMID: 38328403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Management for Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease (RICVD): The 2022 Consensus Statement of the Taiwan Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (TASTRO) and Taiwan Society of Cardiology (TSOC).Acta Cardiol Sin. 2022 Jan;38(1):1-12. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202201_38(1).20211122A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35068877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular disease and cancer: shared risk factors and mechanisms.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Sep;21(9):617-631. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01017-x. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38600368 Review.
-
Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease: The Conjoined Twins.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;16(8):1450. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081450. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shen L, Jhund PS, Petrie MC, Claggett BL, Barlera S, Cleland JGF, Dargie HJ, Granger CB, Kjekshus J, Køber L, Latini R, Maggioni AP, Packer M, Pitt B, Solomon SD, Swedberg K, Tavazzi L, Wikstrand J, Zannad F, Zile MR, McMurray JJ. Declining risk of sudden death in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2017;377:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Moliner P, Lupon J, de Antonio M, Domingo M, Santiago‐Vacas E, Zamora E, Cediel G, Santesmases J, Díez‐Quevedo C, Troya MI, Boldó M, Altmir S, Alonso N, González B, Núñez J, Bayes‐Genis A. Trends in modes of death in heart failure over the last two decades: less sudden death but cancer deaths on the rise. Eur J Heart Fail 2019;21:1259–1266. - PubMed
-
- Meijers WC, Maglione M, Bakker SJ, Oberhuber R, Kieneker LM, de Jong S, Haubner BJ, Nagengast WB, Lyon AR, van der Vegt B, van Veldhuisen DJ, Westenbrink BD, van der Meer P, Silljé HH, de Boer RA. Heart failure stimulates tumor growth by circulating factors. Circulation 2018;138:678–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

