Isolation of dominant Arabidopsis seiv mutants defective in VND7-induced xylem vessel cell differentiation
- PMID: 33088194
- PMCID: PMC7557666
- DOI: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.20.0427a
Isolation of dominant Arabidopsis seiv mutants defective in VND7-induced xylem vessel cell differentiation
Abstract
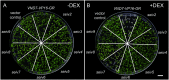
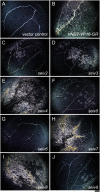
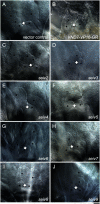
The plant-specific NAC transcription factor VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN 7 (VND7) functions in xylem vessel cell differentiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. To identify novel factors regulating xylem vessel cell differentiation, we previously performed ethyl methanesulfonate mutagenesis of a transgenic 35S::VND7-VP16-GR line in which VND7 activity can be induced post-translationally by glucocorticoid treatment. We successfully isolated mutants that fail to form ectopic xylem vessel cells named seiv (suppressor of ectopic vessel cell differentiation induced by VND7) mutants. Here, we isolated eight novel dominant seiv mutants: seiv2 to seiv9. In these seiv mutants, ectopic xylem vessel cell differentiation was inhibited in aboveground but not underground tissues. Specifically, the shoot apices of the mutants, containing shoot apical meristems and leaf primordia, completely lacked ectopic xylem vessel cells. In these mutants, the VND7-induced upregulation of downstream genes was reduced, especially in shoots compared to roots. However, endogenous xylem vessel cell formation was not affected in the seiv mutants. Therefore, the seiv mutations identified in this study have repressive effects on cell differentiation in shoot meristematic regions, resulting in inhibited ectopic xylem vessel cell differentiation.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; VND7; seiv mutants; xylem vessel cell.
© 2020 Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein S-Nitrosylation Regulates Xylem Vessel Cell Differentiation in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;59(1):17-29. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx151. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29040725
-
VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 directly regulates the expression of a broad range of genes for xylem vessel formation.Plant J. 2011 May;66(4):579-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04514.x. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21284754
-
Histone Deacetylation Controls Xylem Vessel Cell Differentiation via Transcriptional Regulation of a Transcription Repressor Complex OFP1/4-MYB75-KNAT7-BLH6.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 27;12:825810. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.825810. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35154217 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of xylem vessel cell differentiation in VND7-inducible tobacco BY-2 cells by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2018;35(1):31-37. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.18.0129a. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 31275035 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of vascular cell fates.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2010 Dec;13(6):670-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2010.08.011. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20869293 Review.
Cited by
-
Active protein ubiquitination regulates xylem vessel functionality.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 3;36(9):3298-3317. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae221. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 39092875 Free PMC article.
-
scPlant: A versatile framework for single-cell transcriptomic data analysis in plants.Plant Commun. 2023 Sep 11;4(5):100631. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100631. Epub 2023 May 29. Plant Commun. 2023. PMID: 37254480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avci U, Earl Petzold H, Ismail IO, Beers EP, Haigler CH (2008) Cysteine proteases XCP1 and XCP2 aid micro-autolysis within the intact central vacuole during xylogenesis in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 56: 303–315 - PubMed
-
- Bell CJ, Ecker JR (1994) Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19: 137–144 - PubMed
-
- Bollhöner B, Zhang B, Stael S, Denancé N, Overmyer K, Goffner D, Van Breusegem F, Tuominen H (2013) Post mortem function of AtMC9 in xylem vessel elements. New Phytol 200: 498–510 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
