Withaferin-A Treatment Alleviates TAR DNA-Binding Protein-43 Pathology and Improves Cognitive Function in a Mouse Model of FTLD
- PMID: 33078279
- PMCID: PMC8116414
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-020-00952-0
Withaferin-A Treatment Alleviates TAR DNA-Binding Protein-43 Pathology and Improves Cognitive Function in a Mouse Model of FTLD
Abstract
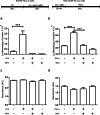
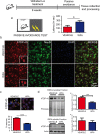
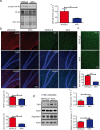
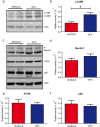
Withaferin-A, an active withanolide derived from the medicinal herbal plant Withania somnifera induces autophagy, reduces TDP-43 proteinopathy, and improves cognitive function in transgenic mice expressing mutant TDP-43 modelling FTLD. TDP-43 is a nuclear DNA/RNA-binding protein with cellular functions in RNA transcription and splicing. Abnormal cytoplasmic aggregates of TDP-43 occur in several neurodegenerative diseases including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), and limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE). To date, no effective treatment is available for TDP-43 proteinopathies. Here, we tested the effects of withaferin-A (WFA), an active withanolide extracted from the medicinal herbal plant Withania somnifera, in a transgenic mouse model of FTLD expressing a genomic fragment encoding mutant TDP-43G348C. WFA treatment ameliorated the cognitive performance of the TDP-43G348C mice, and it reduced NF-κB activity and neuroinflammation in the brain. WFA alleviated TDP-43 pathology while it boosted the levels of the autophagic marker LC3BII in the brain. These data suggest that WFA and perhaps other autophagy inducers should be considered as potential therapy for neurodegenerative diseases with TDP-43 pathology.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; NF-κB; TDP-43; Withania somnifera; autophagy; frontotemporal dementia; withaferin-A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Withania somnifera Reverses Transactive Response DNA Binding Protein 43 Proteinopathy in a Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration.Neurotherapeutics. 2017 Apr;14(2):447-462. doi: 10.1007/s13311-016-0499-2. Neurotherapeutics. 2017. PMID: 27928708 Free PMC article.
-
Data-driven neuropathological staging and subtyping of TDP-43 proteinopathies.Brain. 2023 Jul 3;146(7):2975-2988. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad145. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37150879 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of ALS Pathology by Neuron-Specific Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling.J Neurosci. 2020 Jun 24;40(26):5137-5154. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0536-20.2020. Epub 2020 May 26. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32457070 Free PMC article.
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a spectrum of TDP-43 proteinopathies.Neuropathology. 2010 Apr;30(2):103-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2009.01091.x. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Neuropathology. 2010. PMID: 20102519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial TDP-43 and TDP-43 induced glial pathology, focus on neurodegenerative proteinopathy syndromes.Glia. 2022 Feb;70(2):239-255. doi: 10.1002/glia.24096. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Glia. 2022. PMID: 34558120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium-calcium exchanger isoform-3 targeted Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal therapeutic intervention ameliorates cognition in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 27;12(1):1537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05568-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35087161 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Opportunities of Targeting Astrocytes to Halt Neurodegenerative Disorders.Cells. 2021 Aug 7;10(8):2019. doi: 10.3390/cells10082019. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of Adaptogens: A Mini-Review.Molecules. 2024 Feb 15;29(4):866. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040866. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Therapies and Novel Targets for TDP-43 Proteinopathy in ALS/FTD.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Jul;19(4):1061-1084. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01260-5. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 35790708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of NF-κB with an Analog of Withaferin-A Restores TDP-43 Homeostasis and Proteome Profiles in a Model of Sporadic ALS.Biomedicines. 2024 May 5;12(5):1017. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051017. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buratti E. Functional significance of TDP-43 mutations in disease. Advances in genetics. 91: Elsevier; 2015. p. 1-53. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(3):602–611. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

