A parallel-group, multicenter randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3, clinical trial to test the efficacy of pyridostigmine bromide at low doses to reduce mortality or invasive mechanical ventilation in adults with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: the Pyridostigmine In Severe COvid-19 (PISCO) trial protocol
- PMID: 33066761
- PMCID: PMC7563903
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05485-7
A parallel-group, multicenter randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3, clinical trial to test the efficacy of pyridostigmine bromide at low doses to reduce mortality or invasive mechanical ventilation in adults with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: the Pyridostigmine In Severe COvid-19 (PISCO) trial protocol
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), may lead to severe systemic inflammatory response, pulmonary damage, and even acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This in turn may result in respiratory failure and in death. Experimentally, acetylcholine (ACh) modulates the acute inflammatory response, a neuro-immune mechanism known as the inflammatory reflex. Recent clinical evidence suggest that electrical and chemical stimulation of the inflammatory reflex may reduce the burden of inflammation in chronic inflammatory diseases. Pyridostigmine (PDG), an ACh-esterase inhibitor (i-ACh-e), increases the half-life of endogenous ACh, therefore mimicking the inflammatory reflex. This clinical trial is aimed at evaluating if add-on of PDG leads to a decrease of invasive mechanical ventilation and death among patients with severe COVID-19.
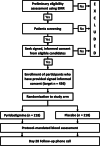
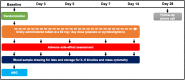
Methods: A parallel-group, multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 clinical trial to test the efficacy of pyridostigmine bromide 60 mg/day P.O. to reduce the need for invasive mechanical ventilation and mortality in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19.
Discussion: This study will provide preliminary evidence of whether or not -by decreasing systemic inflammation- add-on PDG can improve clinical outcomes in patients with severe COVID-19.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04343963 (registered on April 14, 2020).
Keywords: ACh; COVID-19; Immunomodulation; Inflammatory reflex; Invasive mechanical ventilation; Mortality; Placebo-controlled trial; Pyridostigmine; SARS-Cov-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Pablo F Belaunzarán-Zamudio is an Associated Editor for the HIV and co-infections section of BMC Infectious Diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyridostigmine reduces mortality of patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A phase 2/3 randomized controlled trial.Mol Med. 2022 Nov 8;28(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00553-x. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36348276 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Azithromycin added to hydroxychloroquine for patients admitted to intensive care due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-protocol of randomised controlled trial AZIQUINE-ICU.Trials. 2020 Jul 8;21(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04566-x. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32641163 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective, randomized, controlled study assessing vagus nerve stimulation using the gammaCore®-Sapphire device for patients with moderate to severe CoViD-19 Respiratory Symptoms (SAVIOR): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial".Trials. 2020 Jun 26;21(1):576. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04486-w. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32586395 Free PMC article.
-
Computing the Effects of SARS-CoV-2 on Respiration Regulatory Mechanisms in COVID-19.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Aug 19;11(16):2416-2421. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00349. Epub 2020 Aug 11. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32600045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation, Thrombosis, and Destruction: The Three-Headed Cerberus of Trauma- and SARS-CoV-2-Induced ARDS.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:584514. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584514. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33101314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Old drugs, new tricks: leveraging known compounds to disrupt coronavirus-induced cytokine storm.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2022 Oct 10;8(1):38. doi: 10.1038/s41540-022-00250-9. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2022. PMID: 36216820 Free PMC article.
-
Pyridostigmine reduces mortality of patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A phase 2/3 randomized controlled trial.Mol Med. 2022 Nov 8;28(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00553-x. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36348276 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The evolving obesity challenge: targeting the vagus nerve and the inflammatory reflex in the response.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jun;222:107794. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107794. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33310156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal clinical phenotyping of post COVID condition in Mexican adults recovering from severe COVID-19: a prospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 24;10:1236702. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1236702. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37727759 Free PMC article.
-
TREATMENT OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS PATIENTS WITH COVID-19: REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE.Acta Clin Croat. 2022 Feb;60(3):496-509. doi: 10.20471/acc.2021.60.03.21. Acta Clin Croat. 2022. PMID: 35282492 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valdés-Ferrer SI. The challenges of long-term sepsis survivors: when surviving is just the beginning. Rev Investig Clin. 2014;66:439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

