FGFR4 Inhibitor BLU9931 Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion While Inducing Senescence: Evidence for Senolytic Therapy Potential in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 33066597
- PMCID: PMC7602396
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12102976
FGFR4 Inhibitor BLU9931 Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion While Inducing Senescence: Evidence for Senolytic Therapy Potential in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
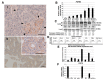
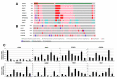
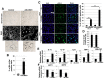
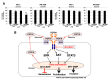
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4), one of four tyrosine kinase receptors for FGFs, is involved in diverse cellular processes. Activation of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling is closely associated with cancer development and progression. In this study, we examined the expression and roles of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). In human PDAC cases, FGFR4 expression positively correlated with larger primary tumors and more advanced stages. Among eight PDAC cell lines, FGFR4 was expressed at the highest levels in PK-1 cells, in which single-nucleotide polymorphism G388R in FGFR4 was detected. For inhibition of autocrine/paracrine FGF19/FGFR4 signaling, we used BLU9931, a highly selective FGFR4 inhibitor. Inhibition of signal transduction through ERK, AKT, and STAT3 pathways by BLU9931 reduced proliferation in FGF19/FGFR4 signaling-activated PDAC cells. By contrast, BLU9931 did not alter stemness features, including stemness marker expression, anticancer drug resistance, and sphere-forming ability. However, BLU9931 inhibited cell invasion, in part, by downregulating membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 in FGF19/FGFR4 signaling-activated PDAC cells. Furthermore, downregulation of SIRT1 and SIRT6 by BLU9931 contributed to senescence induction, priming these cells for quercetin-induced death, a process termed senolysis. Thus, we propose that BLU9931 is a promising therapeutic agent in FGFR4-positive PDAC, especially when combined with senolysis (195/200).
Keywords: FGFR4; FGFR4 inhibitor; growth; invasion; pancreatic cancer; senescence; senolytic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
First Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of FGFR4 for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinomas with an Activated FGFR4 Signaling Pathway.Cancer Discov. 2015 Apr;5(4):424-37. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1029. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25776529
-
Overexpression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 in high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2011 Jan;38(1):133-43. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21109934
-
FGFR4 provides the conduit to facilitate FGF19 signaling in breast cancer progression.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Nov;57(11):1616-1625. doi: 10.1002/mc.22884. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 30074276
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Targeting in Cancer: New Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2019 Jan 9;8(1):31. doi: 10.3390/cells8010031. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30634399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the Role of the FGF19-FGFR4 Signaling Pathway in Cancer Development and Progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 20;8:95. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00095. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32154250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Senescence of Tumor Cells in Anticancer Therapy-Beneficial and Detrimental Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 21;23(19):11082. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911082. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Turning towards nonimmunoreactive tumors: Evaluation of cancer-associated fibroblasts enables prediction of the immune microenvironment and treatment sensitivity in pancreatic cancer.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jul 20;20:3911-3923. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.07.029. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35950187 Free PMC article.
-
FGF19 induces the cell cycle arrest at G2-phase in chondrocytes.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jul 15;9(1):250. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01543-6. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37454120 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1 increases cellular invasion of colorectal neuroendocrine carcinoma cell line through partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Mar 1;30:101239. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101239. eCollection 2022 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 35252596 Free PMC article.
-
Gangliosides as Signaling Regulators in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 11;22(10):5076. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105076. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Korc M., Jeon C.Y., Edderkaoui M., Pandol S.J., Petrov M.S. Consortium for the study of chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, and pancreatic cancer (CPDPC). Tobacco and alcohol as risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017;31:529–536. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahrendt S.A., Pitt H.A. Surgical management of pancreatic cancer. Oncology. 2002;16:725–734. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

