Comparison of Different HILIC Stationary Phases in the Separation of Hemopexin and Immunoglobulin G Glycopeptides and Their Isomers
- PMID: 33065988
- PMCID: PMC7594091
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25204655
Comparison of Different HILIC Stationary Phases in the Separation of Hemopexin and Immunoglobulin G Glycopeptides and Their Isomers
Abstract
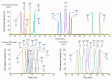
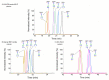
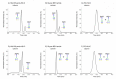
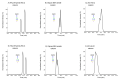
Protein glycosylation analysis is challenging due to the structural variety of complex conjugates. However, chromatographically separating glycans attached to tryptic peptides enables their site-specific characterization. For this purpose, we have shown the importance of selecting a suitable hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) stationary phase in the separation of glycopeptides and their isomers. Three different HILIC stationary phases, i.e., HALO® penta-HILIC, Glycan ethylene bridged hybrid (BEH) Amide, and ZIC-HILIC, were compared in the separation of complex N-glycopeptides of hemopexin and Immunoglobulin G glycoproteins. The retention time increased with the polarity of the glycans attached to the same peptide backbone in all HILIC columns tested in this study, except for the ZIC-HILIC column when adding sialic acid to the glycan moiety, which caused electrostatic repulsion with the negatively charged sulfobetaine functional group, thereby decreasing retention. The HALO® penta-HILIC column provided the best separation results, and the ZIC-HILIC column the worst. Moreover, we showed the potential of these HILIC columns for the isomeric separation of fucosylated and sialylated glycoforms. Therefore, HILIC is a useful tool for the comprehensive characterization of glycoproteins and their isomers.
Keywords: glycopeptide separation; glycopeptides; glycoproteomics; hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography; separation of glycopeptide isomers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography in the separation of glycopeptides and their isomers.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Aug;410(20):5001-5008. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1150-3. Epub 2018 May 28. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29806066 Free PMC article.
-
Separation of isomeric 2-aminopyridine derivatized N-glycans and N-glycopeptides of human serum immunoglobulin G by using a zwitterionic type of hydrophilic-interaction chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2006 Apr 28;1113(1-2):177-81. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.02.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. J Chromatogr A. 2006. PMID: 16503336
-
Comparison of human IgG glycopeptides separation using mixed-mode hydrophilic interaction/ion-exchange liquid chromatography and reversed-phase mode.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Jul;413(16):4321-4328. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03388-3. Epub 2021 May 17. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34002272
-
A review of intact glycopeptide enrichment and glycan separation through hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography stationary phase materials.J Chromatogr A. 2024 Oct 25;1735:465318. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465318. Epub 2024 Aug 31. J Chromatogr A. 2024. PMID: 39244913 Review.
-
Recent development in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography stationary materials for glycopeptide analysis.Anal Methods. 2022 Nov 18;14(44):4437-4448. doi: 10.1039/d2ay01369j. Anal Methods. 2022. PMID: 36300821 Review.
Cited by
-
LC-MS/MS Quantitation of HILIC-Enriched N-glycopeptides Derived from Low-Abundance Serum Glycoproteins in Patients with Narcolepsy Type 1.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 28;13(11):1589. doi: 10.3390/biom13111589. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002271 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the structural resolution of glycosylation microheterogeneity in therapeutic proteins by salt-free hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2395503. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2395503. Epub 2024 Aug 27. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39192481 Free PMC article.
-
The glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2 and its receptor ACE2.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Nov 15;6(1):396. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00809-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34782609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimized Sample Preparation and Microscale Separation Methods for High-Sensitivity Analysis of Hydrophilic Peptides.Molecules. 2022 Oct 6;27(19):6645. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196645. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235181 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for quantification of glycopeptides by liquid separation and mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 Mar;42(2):887-917. doi: 10.1002/mas.21771. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 35099083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Varki A., Cummings R.D., Esko J.D., Stanley P., Hart G., Aebi M., Darvill A.G., Kinoshita T., Packer N.H. Essentials of Glycobiology. 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; New York, NY, USA: 2017. - PubMed
-
- Lisowska E., Jaskiewicz E. Protein Glycosylation, an overview. eLS. 2012 doi: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0006211.pub3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

