Hepatic stem cell Numb gene is a potential target of Huang Qi Decoction against cholestatic liver fibrosis
- PMID: 33060633
- PMCID: PMC7566460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74324-1
Hepatic stem cell Numb gene is a potential target of Huang Qi Decoction against cholestatic liver fibrosis
Abstract
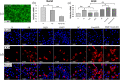
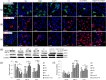
Numb is a negative regulator of Notch signal pathway. Previous study has demonstrated that Notch signal pathway activation is required for hepatic progenitor cell (HPC) differentiating into cholangiocytes in cholestatic liver fibrosis (CLF), and Huang Qi Decoction (HQD) could prevent CLF through inhibition of the Notch signal pathway. However, the role of Numb in HQD against CLF is yet unclear. Thus, CLF rats transplanted into rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells with knocked down Numb gene (BMSCNumb-KD) were treated with HQD. Simultaneously, Numb gene knockdown was also performed in WB-F344 cell line and then treated with refined HQD in vitro. In vivo study revealed that liver fibrosis was inhibited by HQD plus BMSCNumb-KD treatment, while Hyp content in liver tissue, the gene and protein expression of α-SMA, gene expression of Col I, TNF-α, and TGF-β1 were increased compared to that in HQD group. Furthermore, Notch signal pathway was inhibited by HQD plus BMSCNumb-KD, while the protein expression of Numb was decreased and RBP-Jκ and Hes1 was increased compared to that in HQD group. In vitro, HQD reduced the differentiation of WB-F344 cells into cholangiocyte phenotype, while this effect was attenuated after Numb-knockdown. This study highlights that the absence of hepatic stem cell Numb gene decreases effect of HQD against CLF, which give rise the conclusion that Numb might be a potential target for HQD against CLF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BM-MSCs overexpressing the Numb enhance the therapeutic effect on cholestatic liver fibrosis by inhibiting the ductular reaction.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Mar 20;14(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03276-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36941658 Free PMC article.
-
Huang Qi Decoction Prevents BDL-Induced Liver Fibrosis Through Inhibition of Notch Signaling Activation.Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(1):85-104. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500070. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Am J Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 28081630
-
[Mechanism of Astragaloside prevents cholestatic liver fibrosis through inhibition of Notch signaling activation].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 20;25(8):575-582. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.08.005. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29056006 Chinese.
-
Promising traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cholestatic liver disease process (cholestasis, hepatitis, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;297:115550. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115550. Epub 2022 Jul 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35863612 Review.
-
Advances in anti hepatic fibrotic therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine herbal formula.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 6;251:112442. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112442. Epub 2019 Dec 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31891799 Review.
Cited by
-
Astragalus saponins and its main constituents ameliorate ductular reaction and liver fibrosis in a mouse model of DDC-induced cholestatic liver disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 20;13:965914. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.965914. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339578 Free PMC article.
-
Potential therapeutic targets and biological mechanisms of Centella asiatica on hepatic fibrosis: a study of network pharmacology.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jun;9(11):932. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2253. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34350247 Free PMC article.
-
Astragalus and its formulas as a therapeutic option for fibrotic diseases: Pharmacology and mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 3;13:1040350. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1040350. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36408254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit hepatic fibrosis via the AABR07028795.2/rno-miR-667-5p axis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 28;13(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03069-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35902883 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

