CytoGPS: A large-scale karyotype analysis of CML data
- PMID: 33059160
- PMCID: PMC8126981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2020.09.005
CytoGPS: A large-scale karyotype analysis of CML data
Abstract
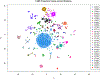
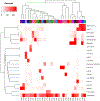
Karyotyping, the practice of visually examining and recording chromosomal abnormalities, is commonly used to diagnose diseases of genetic origin, including cancers. Karyotypes are recorded as text written in the International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN). Downstream analysis of karyotypes is conducted manually, due to the visual nature of analysis and the linguistic structure of the ISCN. The ISCN has not been computer-readable and, as such, prevents the full potential of these genomic data from being realized. In response, we developed CytoGPS, a platform to analyze large volumes of cytogenetic data using a Loss-Gain-Fusion model that converts the human-readable ISCN karyotypes into a machine-readable binary format. As proof of principle, we applied CytoGPS to cytogenetic data from the Mitelman Database of Chromosome Aberrations and Gene Fusions in Cancer, a National Cancer Institute hosted database of over 69,000 karyotypes of human cancers. Using the Jaccard coefficient to determine similarity between karyotypes structured as binary vectors, we were able to identify novel patterns from 4,968 Mitelman CML karyotypes, such as the co-occurrence of trisomy 19 and 21. The CytoGPS platform unlocks the potential for large-scale, comparative analysis of cytogenetic data. This methodological platform is freely available at CytoGPS.org.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Chronic myeloid leukemia; CytoGPS; Cytogenetics; Data science; Karyotypes.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RCytoGPS: an R package for reading and visualizing cytogenetics data.Bioinformatics. 2021 Dec 7;37(23):4589-4590. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab683. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34601554 Free PMC article.
-
CytoGPS: a web-enabled karyotype analysis tool for cytogenetics.Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec 15;35(24):5365-5366. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz520. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31263896 Free PMC article.
-
Text Mining and Data Modeling of Karyotypes to aid in Drug Repurposing Efforts.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;216:1037. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015. PMID: 26262336 Free PMC article.
-
Relapse and cytogenetic evolution in myeloid neoplasms.Panminerva Med. 2017 Dec;59(4):308-319. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.17.03380-8. Panminerva Med. 2017. PMID: 29144072 Review.
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia with complex karyotypes: Prognosis and therapeutic approaches.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5798-5806. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27505. Epub 2018 Nov 14. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30430567 Review.
Cited by
-
RCytoGPS: an R package for reading and visualizing cytogenetics data.Bioinformatics. 2021 Dec 7;37(23):4589-4590. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab683. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34601554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shuman S, Structure, mechanism, and evolution of the mRNA capping apparatus. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol, 2001. 66: p. 1–40. - PubMed
-
- Heim S and Mitelman F, Cancer cytogenetics: chromosomal and molecular genetic aberrations of tumor cells. 2015: John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Stevens-Kroef M, et al., Cytogenetic Nomenclature and Reporting. Methods Mol Biol, 2017. 1541: p. 303–309. - PubMed
-
- Hiller B, et al., CyDAS: a cytogenetic data analysis system. Bioinformatics, 2005. 21(7): p. 1282–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

