Epigenomic Evaluation of Cholangiocyte Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Identifies a Selective Role for Histone 3 Lysine 9 Acetylation in Biliary Fibrosis
- PMID: 33058867
- PMCID: PMC7878301
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.008
Epigenomic Evaluation of Cholangiocyte Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Identifies a Selective Role for Histone 3 Lysine 9 Acetylation in Biliary Fibrosis
Abstract
Background & aims: Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) upregulates cholangiocyte-derived signals that activate myofibroblasts and promote fibrosis. Using epigenomic and transcriptomic approaches, we sought to distinguish the epigenetic activation mechanisms downstream of TGFβ that mediate transcription of fibrogenic signals.
Methods: Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-seq and RNA-seq were performed to assess histone modifications and transcriptional changes following TGFβ stimulation. Histone modifications and acetyltransferase occupancy were confirmed using ChIP assays. Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) was used to investigate changes in chromatin accessibility. Cholangiocyte cell lines and primary cholangiocytes were used for in vitro studies. Mdr2-/- and 3,5-diethoxycarboncyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine (DDC)-fed mice were used as animal models.
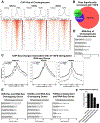
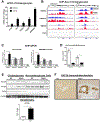
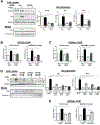
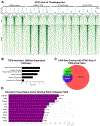
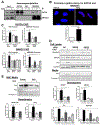
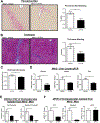
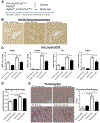
Results: TGFβ stimulation caused widespread changes in histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac), and was associated with global TGFβ-mediated transcription. In contrast, H3K9ac was gained in a smaller group of chromatin sites and was associated with fibrosis pathways. These pathways included overexpression of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activators such as fibronectin 1 (FN1) and SERPINE1. The promoters of these genes showed H3K9ac enrichment following TGFβ. Of the acetyltransferases responsible for H3K9ac, cholangiocytes predominantly express Lysine Acetyltransferases 2A (KAT2A). Small interfering RNA knockdown of KAT2A or H3K9ac inhibition prevented the TGFβ-mediated increase in FN1 and SERPINE1. SMAD3 ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq suggested that TGFβ-mediated H3K9ac occurs through SMAD signaling, which was confirmed using colocalization and genetic knockdown studies. Pharmacologic inhibition or cholangiocyte-selective deletion of Kat2a was protective in mouse models of biliary fibrosis.
Conclusions: Cholangiocyte expression of HSC-activating signals occurs through SMAD-dependent, KAT2A-mediated, H3K9ac, and can be targeted to prevent biliary fibrosis.
Keywords: Epigenetics; FN; PAI1.
Copyright © 2021 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aramchol attenuates fibrosis in mouse models of biliary fibrosis and blocks the TGFβ-induced fibroinflammatory mediators in cholangiocytes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 13:2024.11.06.621880. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.06.621880. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39574583 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Epithelial Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Does Not Contribute to Liver Fibrosis but Protects Mice From Cholangiocarcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar;150(3):720-33. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.039. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 26627606 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of integrin alphavbeta6 on cholangiocytes blocks transforming growth factor-beta activation and retards biliary fibrosis progression.Gastroenterology. 2008 Aug;135(2):660-70. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.04.009. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18538673 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GCN5: its biological functions and therapeutic potentials.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Jan 15;135(1):231-257. doi: 10.1042/CS20200986. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33443284 Review.
Cited by
-
Chuanxiong Rhizoma extracts prevent liver fibrosis via targeting CTCF-c-MYC-H19 pathway.Chin Herb Med. 2023 Nov 28;16(1):82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2023.07.003. eCollection 2024 Jan. Chin Herb Med. 2023. PMID: 38375042 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Complex Interplay between Epigenetics and Immunity in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Sep 4;19(15):4811-4830. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.87975. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37781509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNA-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Hepatic Stellate Cells of Liver Fibrosis.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Aug 7;10(4):44. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10040044. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 39195573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA ACTA2-AS1 promotes ductular reaction by interacting with the p300/ELK1 complex.J Hepatol. 2022 Apr;76(4):921-933. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.014. Epub 2021 Dec 23. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34953958 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modification in liver fibrosis: Promising therapeutic direction with significant challenges ahead.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Mar;14(3):1009-1029. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.10.023. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38486982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Santos-Laso A, Munoz-Garrido P, Felipe-Agirre M, et al. New Advances in the Molecular Mechanisms Driving Biliary Fibrosis and Emerging Molecular Targets. Curr Drug Targets 2017;18:908–920. - PubMed
-
- Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. TGF-beta: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol 2016;12:325–38. - PubMed
-
- Pinto C, Giordano DM, Maroni L, et al. Role of inflammation and proinflammatory cytokines in cholangiocyte pathophysiology. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2018;1864:1270–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

