KSHV G-protein coupled receptor vGPCR oncogenic signaling upregulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 expression mediates angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma
- PMID: 33057440
- PMCID: PMC7591070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009006
KSHV G-protein coupled receptor vGPCR oncogenic signaling upregulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 expression mediates angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma
Abstract
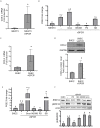
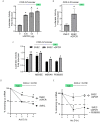
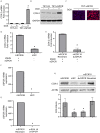
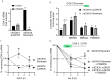
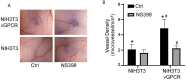
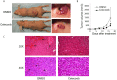
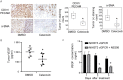
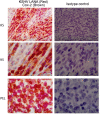
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) vGPCR is a constitutively active G protein-coupled receptor that subverts proliferative and inflammatory signaling pathways to induce cell transformation in Kaposi's sarcoma. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is an inflammatory mediator that plays a key regulatory role in the activation of tumor angiogenesis. Using two different transformed mouse models and tumorigenic full KSHV genome-bearing cells, including KSHV-Bac16 based mutant system with a vGPCR deletion, we demostrate that vGPCR upregulates COX-2 expression and activity, signaling through selective MAPK cascades. We show that vGPCR expression triggers signaling pathways that upregulate COX-2 levels due to a dual effect upon both its gene promoter region and, in mature mRNA, the 3'UTR region that control mRNA stability. Both events are mediated by signaling through ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Inhibition of COX-2 in vGPCR-transformed cells impairs vGPCR-driven angiogenesis and treatment with the COX-2-selective inhibitory drug Celecoxib produces a significant decrease in tumor growth, pointing to COX-2 activity as critical for vGPCR oncogenicity in vivo and indicating that COX-2-mediated angiogenesis could play a role in KS tumorigenesis. These results, along with the overexpression of COX-2 in KS lesions, define COX-2 as a potential target for the prevention and treatment of KSHV-oncogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6 and G-protein-coupled receptor regulate angiopoietin-2 expression in lymphatic endothelial cells.Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;67(9):4042-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3321. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17483315
-
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor as a therapeutic target for the treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma.Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 1;66(1):168-74. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1026. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16397229
-
A role for virally induced reactive oxygen species in Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus tumorigenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Jan 1;18(1):80-90. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4584. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22746102 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2-prostaglandin E2-eicosanoid receptor inflammatory axis: a key player in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus associated malignancies.Transl Res. 2013 Aug;162(2):77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23567332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt/TSC/mTOR activation by the KSHV G protein-coupled receptor: emerging insights into the molecular oncogenesis and treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma.Cell Cycle. 2007 Feb 15;6(4):438-43. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.4.3843. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17329974 Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into the Epigenetics of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14955. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914955. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of DNA Viruses in Human Cancer.Cancer Inform. 2023 Jun 13;22:11769351231154186. doi: 10.1177/11769351231154186. eCollection 2023. Cancer Inform. 2023. PMID: 37363356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A major role for Nrf2 transcription factors in cell transformation by KSHV encoded oncogenes.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 21;12:890825. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.890825. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36212441 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Celecoxib in Addition to Standard Cancer Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 25;29(9):6137-6153. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090482. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Studies of Pegylated Magnetite Nanoparticles in a Cellular Model of Viral Oncogenesis: Initial Studies to Evaluate Their Potential as a Future Theranostic Tool.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 1;15(2):488. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020488. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ensoli B, Sturzl M. Kaposi’s sarcoma: a result of the interplay among inflammatory cytokines, angiogenic factors and viral agents. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 1998;9(1):63–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

