Cytokine Storms in Cancer and COVID-19
- PMID: 33038939
- PMCID: PMC7531591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.019
Cytokine Storms in Cancer and COVID-19
Abstract
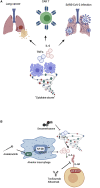
During the COVID-19 pandemic, research on "cytokine storms" has been reinvigorated in the field of infectious disease, but it also has particular relevance to cancer research. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has emerged as a key component of the immune response to SARS-CoV-2, such that the repurposing of anti-IL-6 therapeutics for COVID-19 is now a major line of investigation, with several ongoing clinical trials. We lay a framework for understanding the role of IL-6 in the context of cancer research and COVID-19 and suggest how lessons learned from cancer research may impact SARS-CoV-2 research and vice versa.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2: a storm is raging.J Clin Invest. 2020 May 1;130(5):2202-2205. doi: 10.1172/JCI137647. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32217834 Free PMC article.
-
Immunologic Features in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Functional Exhaustion of T Cells and Cytokine Storm.J Clin Immunol. 2020 Oct;40(7):974-976. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00824-4. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32648027 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Immune-Engaging Cancer Treatment.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Oct 1;6(10):1529-1530. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2367. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32433719 No abstract available.
-
Cytokine Storms: Understanding COVID-19.Immunity. 2020 Jul 14;53(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017. Epub 2020 Jun 28. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32610079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages.Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Jun;20(6):355-362. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4. Epub 2020 May 6. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32376901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro analysis suggests that SARS-CoV-2 infection differentially modulates cancer-like phenotypes and cytokine expression in colorectal and prostate cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 19;14(1):24625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75718-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39427065 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Storm Syndrome Associated with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1448:323-353. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-59815-9_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39117825 Review.
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome is essential for IL-18 production in a murine model of macrophage activation syndrome.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Jul 1;17(7):dmm050762. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050762. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 38775430 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from SARS-CoV-2 M-protein-induced triple negative breast cancer cells promoted the ability of tissue stem cells supporting cancer progression.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 7;14:1346312. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1346312. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38515582 Free PMC article.
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome is essential for IL-18 production in a murine model of macrophage activation syndrome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 1:2024.02.27.582284. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.27.582284. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Dis Model Mech. 2024 Jul 1;17(7):dmm050762. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050762. PMID: 38464243 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Balkwill F., Charles K.A., Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:211–217. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

