Endothelium-Independent Vasodilatory Effect of Sailuotong (SLT) on Rat Isolated Tail Artery
- PMID: 33029174
- PMCID: PMC7527950
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8125805
Endothelium-Independent Vasodilatory Effect of Sailuotong (SLT) on Rat Isolated Tail Artery
Abstract
Background: Sailuotong (SLT) is a standardized three-herb formulation consisting of extracts of Panax ginseng, Ginkgo biloba, and Crocus sativus for the treatment of vascular dementia (VaD). Although SLT has been shown to increase cerebral blood flow, the direct effects of SLT on vascular reactivity have not been explored. This study aims to examine the vasodilatory effects of SLT and the underlying mechanisms in rat isolated tail artery.
Methods: Male (250-300 g) Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rat tail artery was isolated for isometric tension measurement. The effects of SLT on the influx of calcium through the cell membrane calcium channels were determined in Ca2+-free solution experiments.
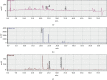
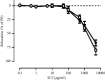
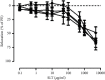
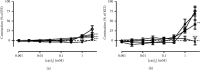
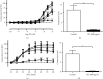
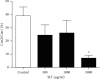
Results: SLT (0.1-5,000 μg/ml) caused a concentration-dependent relaxation in rat isolated tail artery precontracted by phenylephrine. In the contraction experiments, SLT (500, 1,000, and 5,000 μg/mL) significantly inhibited phenylephrine (0.001 to 10 μM)- and KCl (10-80 mM)-induced contraction, in a concentration-dependent manner. In Ca2+-free solution, SLT (500, 1,000, and 5,000 μg/mL) markedly suppressed Ca2+-induced (0.001-3 mM) vasoconstriction in a concentration-dependent manner in both phenylephrine (10 μM) or KCl (80 mM) stimulated tail arteries. L-type calcium channel blocker nifedipine (10 μM) inhibited PE-induced contraction. Furthermore, SLT significantly reduced phenylephrine-induced transient vasoconstriction in the rat isolated tail artery.
Conclusion: SLT induces relaxation of rat isolated tail artery through endothelium-independent mechanisms. The SLT-induced vasodilatation appeared to be jointly meditated by blockages of extracellular Ca2+ influx via receptor-gated and voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and inhibition of the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Copyright © 2020 S. Y. Yeon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
As a medical research institute, NICM Health Research Institute receives research grants and donations from foundations, universities, government agencies, individuals, and industry. Sponsors and donors also provide untied funding for work to advance the vision and mission of the institute. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ion channel mechanisms of rat tail artery contraction-relaxation by menthol involving, respectively, TRPM8 activation and L-type Ca2+ channel inhibition.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Dec 1;311(6):H1416-H1430. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00222.2015. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27765744 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated administration of Sailuotong, a fixed combination of Panax ginseng, Ginkgo biloba, and Crocus sativus extracts for vascular dementia, alters CYP450 activities in rats.Phytomedicine. 2018 Jan 1;38:125-134. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29425645
-
Mechanism of Membrane Depolarization Involved in α1A-Adrenoceptor-Mediated Contraction in Rat Tail and Iliac Arteries.Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(10):1741-1745. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00473. Biol Pharm Bull. 2019. PMID: 31582662
-
The Curcumin-Induced Vasorelaxation in Rat Superior Mesenteric Arteries.Ann Vasc Surg. 2018 Apr;48:233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Ann Vasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 28943490
-
Paeonol induces vasodilatation in rat mesenteric artery via inhibiting extracellular Ca²⁺ influx and intracellular Ca²⁺ release.Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Jul;19(7):510-6. doi: 10.1007/s11655-013-1505-8. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Chin J Integr Med. 2013. PMID: 23818203
Cited by
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group 12-week pilot phase II trial of SaiLuoTong (SLT) for cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2023 Oct 11;9(4):e12420. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12420. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37830013 Free PMC article.
-
A review of SaiLuoTong (MLC-SLT) development in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 1;15:1343820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1343820. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38751782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Santos C. Y., Snyder P. J., Wu W. C., Zhang M., Echeverria A., Alber J. Pathophysiologic relationship between alzheimer’s disease, cerebrovascular disease, and cardiovascular risk: a review and synthesis. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring. 2017;7(1):69–87. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2017.01.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

