Novel insights on targeting ferroptosis in cancer therapy
- PMID: 33024562
- PMCID: PMC7532638
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-020-00229-w
Novel insights on targeting ferroptosis in cancer therapy
Abstract
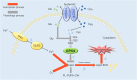
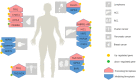
Ferroptosis belongs to a novel form of regulated cell death. It is characterized by iron dependence, destruction of intracellular redox balance and non-apoptosis. And cellular structure and molecules level changes also occur abnormally during ferroptosis. It has been proved that ferroptosis exist widespreadly in many diseases, such as heart disease, brain damage or alzheimer disease. At the same time, the role of ferroptosis in cancer cannot be underestimated. More and more indications have told that ferroptosis is becoming a powerful weapon against cancer. In addition, therapies rely on ferroptosis have been applied to the clinic. Therefore, it is necessary to understand this newly discovered form of cell death and its connection with cancer. This review summarizes the mechanism of ferroptosis, ferroptosis inducers based on different targets and inspection methods. At last, we analyzed the relationship between ferroptosis and malignancies, in order to provide a novel theory basis for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; Ferroptosis; Signaling pathway; Therapy.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Ferroptosis Pathways: A Novel Strategy for Cancer Therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022;22(3):234-244. doi: 10.2174/1568009622666220211122745. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 35152865 Review.
-
Targeting ferroptosis for cancer therapy: exploring novel strategies from its mechanisms and role in cancers.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Aug;9(4):1569-1584. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-341. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32953528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Ferroptosis Inducers for Cancer Therapy.Adv Mater. 2019 Dec;31(51):e1904197. doi: 10.1002/adma.201904197. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31595562 Review.
-
The role of ferroptosis in esophageal cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Aug 23;22(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02685-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35999642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis and Cancer: Complex Relationship and Potential Application of Exosomes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 8;9:733751. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.733751. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights into Ferroptosis Initiating Therapies (FIT) by Targeting the Rewired Lipid Metabolism in Ovarian Cancer Peritoneal Metastases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 3;23(23):15263. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315263. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Prognostic Ferroptosis-Related lncRNA Signature Associated with Immune Landscape in Invasive Breast Cancer.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 20;2022:9168556. doi: 10.1155/2022/9168556. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35359880 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestrated Action of AMPK Activation and Combined VEGF/PD-1 Blockade with Lipid Metabolic Tunning as Multi-Target Therapeutics against Ovarian Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 20;23(12):6857. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126857. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Macrophages in Atherogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 26;12:785220. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.785220. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis Holds Novel Promise in Treatment of Cancer Mediated by Non-coding RNAs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 21;9:686906. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.686906. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34235152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ursini F, Maiorino M, Valente M, Ferri L, Gregolin C. Purification from pig liver of a protein which protects liposomes and biomembranes from peroxidative degradation and exhibits glutathione peroxidase activity on phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982;710:197–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90150-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

