Metabolism and Functions of Inositol Pyrophosphates: Insights Gained from the Application of Synthetic Analogues
- PMID: 33023101
- PMCID: PMC7583957
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25194515
Metabolism and Functions of Inositol Pyrophosphates: Insights Gained from the Application of Synthetic Analogues
Abstract
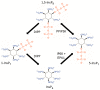
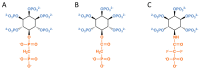
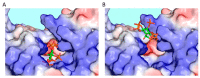
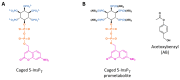
Inositol pyrophosphates (PP-InsPs) comprise an important group of intracellular, diffusible cellular signals that a wide range of biological processes throughout the yeast, plant, and animal kingdoms. It has been difficult to gain a molecular-level mechanistic understanding of the actions of these molecules, due to their highly phosphorylated nature, their low levels, and their rapid metabolic turnover. More recently, these obstacles to success are being surmounted by the chemical synthesis of a number of insightful PP-InsP analogs. This review will describe these analogs and will indicate the important chemical and biological information gained by using them.
Keywords: cell biology; energy; homeostasis; metabolism; phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inositol polyphosphates intersect with signaling and metabolic networks via two distinct mechanisms.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 1;113(44):E6757-E6765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606853113. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27791083 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol pyrophosphates: why so many phosphates?Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:203-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.015. Epub 2014 Oct 5. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25453220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Versatile signaling mechanisms of inositol pyrophosphates.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Oct;70:102177. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102177. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35780751 Review.
-
Phosphate transfer from inositol pyrophosphates InsP5PP and InsP4(PP)2: a semi-empirical investigation.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Jan 1;17(1):183-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.09.066. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007. PMID: 17045478
-
β-lapachone regulates mammalian inositol pyrophosphate levels in an NQO1- and oxygen-dependent manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 22;120(34):e2306868120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2306868120. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37579180 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protein pyrophosphorylation by inositol phosphates: a novel post-translational modification in plants?Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 22;15:1347922. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1347922. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38455731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple substrate recognition by yeast diadenosine and diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase through phosphate clamping.Sci Adv. 2021 Apr 23;7(17):eabf6744. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf6744. Print 2021 Apr. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33893105 Free PMC article.
-
A structural exposé of noncanonical molecular reactivity within the protein tyrosine phosphatase WPD loop.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 25;13(1):2231. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29673-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35468885 Free PMC article.
-
Expedient synthesis and luminescence sensing of the inositol pyrophosphate cellular messenger 5-PP-InsP5.Chem Sci. 2023 Apr 13;14(19):4979-4985. doi: 10.1039/d2sc06812e. eCollection 2023 May 17. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37206391 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Chemical and Biological Insights of Inositol Derivatives in Mediterranean Plants.Molecules. 2022 Feb 24;27(5):1525. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051525. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268625 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

