Identification of nitric oxide (NO)-responsive genes under hypoxia in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) root
- PMID: 33020554
- PMCID: PMC7536229
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73613-z
Identification of nitric oxide (NO)-responsive genes under hypoxia in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) root
Abstract
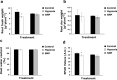
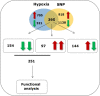
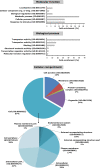
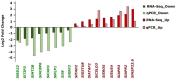
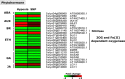
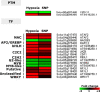
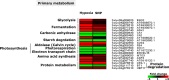
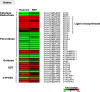
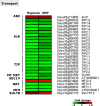
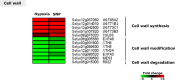
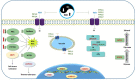
Flooding periods, as one probable consequence of climate change, will lead more frequently to plant hypoxic stress. Hypoxia sensing and signaling in the root, as the first organ encountering low oxygen, is therefore crucial for plant survival under flooding. Nitric oxide has been shown to be one of the main players involved in hypoxia signaling through the regulation of ERFVII transcription factors stability. Using SNP as NO donor, we investigated the NO-responsive genes, which showed a significant response to hypoxia. We identified 395 genes being differentially regulated under both hypoxia and SNP-treatment. Among them, 251 genes showed up- or down-regulation under both conditions which were used for further biological analysis. Functional classification of these genes showed that they belong to different biological categories such as primary carbon and nitrogen metabolism (e.g. glycolysis, fermentation, protein and amino acid metabolism), nutrient and metabolites transport, redox homeostasis, hormone metabolism, regulation of transcription as well as response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Our data shed light on the NO-mediated gene expression modulation under hypoxia and provides potential targets playing a role in hypoxia tolerance. These genes are interesting candidates for further investigating their role in hypoxia signaling and survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RNA-Seq reveals novel genes and pathways associated with hypoxia duration and tolerance in tomato root.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 3;10(1):1692. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57884-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32015352 Free PMC article.
-
The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor SlNAC4 regulates salt and drought tolerance and stress-related genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum).Plant Cell Rep. 2014 Nov;33(11):1851-63. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1662-z. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Plant Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25063324
-
Whirly (Why) transcription factors in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.): genome-wide identification and transcriptional profiling under drought and salt stresses.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Aug;46(4):4139-4150. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04863-y. Epub 2019 May 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31089915
-
Group VII Ethylene Response Factors Coordinate Oxygen and Nitric Oxide Signal Transduction and Stress Responses in Plants.Plant Physiol. 2015 Sep;169(1):23-31. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00338. Epub 2015 May 5. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25944828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide, energy, and redox-dependent responses to hypoxia.J Exp Bot. 2024 Aug 12;75(15):4573-4588. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae139. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38557811 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide, a Key Modulator in the Alleviation of Environmental Stress-Mediated Damage in Crop Plants: A Meta-Analysis.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 26;12(11):2121. doi: 10.3390/plants12112121. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The underestimated role of plant root nitric oxide emission under low-oxygen stress.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 6;15:1290700. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1290700. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38379951 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide and cytokinin cross-talk and their role in plant hypoxia response.Plant Signal Behav. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2329841. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2024.2329841. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Plant Signal Behav. 2024. PMID: 38521996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards genetically encoded sensors for nitric oxide bioimaging in planta.Plant Physiol. 2021 Oct 5;187(2):477-479. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab232. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34608950 Free PMC article.
-
How Extracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Reach Their Intracellular Targets in Plants.Mol Cells. 2023 Jun 30;46(6):329-336. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.2158. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 36799103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

