Study of the Relationship Between Ultrasound Strain Indices and Cognitive Decline for Vulnerable Carotid Plaque
- PMID: 33018417
- PMCID: PMC8063208
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9175911
Study of the Relationship Between Ultrasound Strain Indices and Cognitive Decline for Vulnerable Carotid Plaque
Abstract
A relationship between ultrasound strain indices in carotid plaque to cognitive domains of executive and language function are studied in 42 symptomatic and 34 asymptomatic patients. The mean and standard deviation of the percentage stenosis were 72.10 ± 15.19 and 77.41 ± 11.20 for symptomatic and asymptomatic patients respectively. Pearson's correlation between axial, lateral and shear strain indices versus executive and language composite scores was performed.. A significant inverse correlation for both executive and language function for symptomatic patients to strain indices was found. On the other hand, for asymptomatic patients only executive function was inversely correlated with the corresponding strain indices. Our hypothesis that microemboli from vulnerable plaque and possible 'silent strokes' may be responsible for decline in executive function for both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients'. Strokes and transient ischemic attacks may be responsible for further cognitive decline in language function for symptomatic patients.
Figures
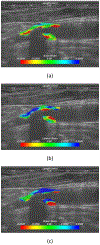
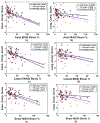
Similar articles
-
A Cross-Sectional Investigation of Cognition and Ultrasound-Based Vascular Strain Indices.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2019 Jan 24;35(1):46-55. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acz006. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2019. PMID: 30805597 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid atherosclerotic plaque instability and cognition determined by ultrasound-measured plaque strain in asymptomatic patients with significant stenosis.J Neurosurg. 2018 Jan;128(1):111-119. doi: 10.3171/2016.10.JNS161299. Epub 2017 Mar 10. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28298048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Correlation of cognitive function with ultrasound strain indices in carotid plaque.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014 Jan;40(1):78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24120415 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary carotid imaging: from degree of stenosis to plaque vulnerability.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):27-42. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26230478 Review.
-
Ultrasound Characteristics of Symptomatic Carotid Plaques: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;40(3-4):165-74. doi: 10.1159/000437339. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26279159 Review.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ et al., “Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association,” Circulation, vol. 137, no. 12, pp. e67–e492, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Céspedes I, Huang Y, Ophir J, and Spratt S, “Methods for estimation of subsample time delays of digitized echo signals,” Ultrason. Imaging, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 142–171, 1995. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
