An ace model for SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 33000129
- PMCID: PMC7522667
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20201748
An ace model for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
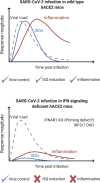
Developing effective in vivo models for SARS-CoV-2 infection is crucial for mechanistic studies of COVID-19 disease progression. In this issue of JEM, Israelow et al. (https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20201241) generate a model that supports SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice, which they use to characterize type I IFN-driven pulmonary inflammation.
© 2020 Major and Wack.
Figures

Comment on
-
Mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 reveals inflammatory role of type I interferon signaling.J Exp Med. 2020 Dec 7;217(12):e20201241. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201241. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32750141 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Sex-biased Immune Responses Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Dec;28(12):952-954. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33077340 Free PMC article.
-
An unconventional view of COVID-19 T cell immunity.J Exp Med. 2020 Dec 7;217(12):e20201727. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201727. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 33147321 Free PMC article.
-
Reply to Peng He, Xiaohui Wang, and Hao Li's Letter to the Editor re: Yu Xiao, Kaiyu Qian, Yongwen Luo, et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Renal Failure Patients: A Potential Covert Source of Infection. Eur Urol. In press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.025.Eur Urol. 2020 Nov;78(5):e203-e204. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.008. Epub 2020 May 13. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32405138 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A comparative overview of COVID-19, MERS and SARS: Review article.Int J Surg. 2020 Sep;81:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.07.032. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32730205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune response in SARS-CoV-2 infection: the role of interferons type I and type III.Braz J Infect Dis. 2020 Sep-Oct;24(5):428-433. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2020.07.011. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Braz J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32866437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic variation, origin tracing, and vaccine development of SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review.Innovation (Camb). 2021 May 28;2(2):100116. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100116. Epub 2021 May 11. Innovation (Camb). 2021. PMID: 33997827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status of Putative Animal Sources of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Humans: Wildlife, Domestic Animals and Pets.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 17;9(4):868. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040868. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33920724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell, C.L., et al. . 2011. J. Clin. Invest. 10.1172/JCI57367 - DOI
-
- Blanco-Melo, D., et al. . 2020. Cell. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026 - DOI
-
- Boudewijns, R., et al. . 2020. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2020.04.23.056838 (Preprint posted July 2, 2020) - DOI
-
- Carlin, A.F., et al. . 2017. Cell Rep. 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.054 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

