Nitric Oxide-Releasing Thermoresponsive Pluronic F127/Alginate Hydrogel for Enhanced Antibacterial Activity and Accelerated Healing of Infected Wounds
- PMID: 32998349
- PMCID: PMC7600256
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12100926
Nitric Oxide-Releasing Thermoresponsive Pluronic F127/Alginate Hydrogel for Enhanced Antibacterial Activity and Accelerated Healing of Infected Wounds
Abstract
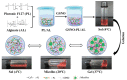
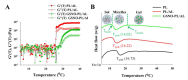
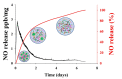
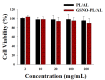
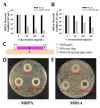
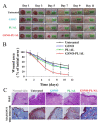
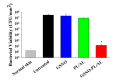
Nitric oxide (NO), a highly reactive and lipophilic molecule, is one of the molecules present in the wound environment and implicated as an important regulator in all phases of wound healing. Here, we developed an NO-releasing thermoresponsive hydrogel (GSNO-PL/AL) composed of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), pluronic F127 (PL), and alginate (AL) for the treatment of infected wounds. The GSNO was incorporated into the thermoresponsive PL/AL hydrogel, and differential scanning calorimetry techniques were used for the hydrogel characterization. The hydrogel was assessed by in vitro NO release, antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity, and wound-healing activity. The GSNO-PL/AL hydrogel demonstrated thermal responsiveness and biocompatibility, and it showed sustained NO release for 7 days. It also exhibited potent bactericidal activity against Gram-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MRPA). Moreover, the GSNO-PL/AL treatment of MRPA-infected wounds accelerated healing with a reduced bacterial burden in the wounds. The GSNO-PL/AL hydrogel would be a promising option for the treatment of infected wounds.
Keywords: S-nitrosoglutathione; antibacterial; infected wound healing; pluronic F127; thermoresponsive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles and current applications of S-nitrosoglutathione in anti-infective biomaterials.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Sep 6;16:100419. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100419. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36105674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocompatible and Antibacterial Nitric Oxide-Releasing Pluronic F-127/Chitosan Hydrogel for Topical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2018 Apr 18;10(4):452. doi: 10.3390/polym10040452. Polymers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30966487 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Delivery Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel with Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Brevilin A and Nitric Oxide for Wound Healing in Bacterial Infection.Gels. 2024 Mar 24;10(4):219. doi: 10.3390/gels10040219. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667638 Free PMC article.
-
In Situ Hydrogel-Forming/Nitric Oxide-Releasing Wound Dressing for Enhanced Antibacterial Activity and Healing in Mice with Infected Wounds.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Sep 27;11(10):496. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11100496. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31569746 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Pluronic F127 Derivatives for Application in Wound Healing and Repair.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Aug 7;18:4485-4505. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S418534. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37576462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles and current applications of S-nitrosoglutathione in anti-infective biomaterials.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Sep 6;16:100419. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100419. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36105674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Advances in the Development of Hydrogel-Based Wound Dressings for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 6;14(14):2764. doi: 10.3390/polym14142764. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric Oxide-Releasing Bacterial Cellulose/Chitosan Crosslinked Hydrogels for the Treatment of Polymicrobial Wound Infections.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 22;14(1):22. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010022. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056917 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hyaluronic Acid and Pluronic-F68 on the Surface Properties of Foam as a Delivery System for Polidocanol in Sclerotherapy.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Oct 30;12(11):1039. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111039. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33143001 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Bioengineered Scaffolds Composed of Thermo-Responsive Polymers for Drug Delivery in Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 30;22(3):1408. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031408. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33573351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scatena R., Bottoni P., Pontoglio A., Giardina B. Pharmacological modulation of nitric oxide release: New pharmacological perspectives, potential benefits and risks. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010;17:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Chen A.F. Nitric oxide: A newly discovered function on wound healing. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005;26:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro L.J. Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2000.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

