Integrated analysis of the transcriptome-wide m6A methylome in preeclampsia and healthy control placentas
- PMID: 32983644
- PMCID: PMC7500358
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9880
Integrated analysis of the transcriptome-wide m6A methylome in preeclampsia and healthy control placentas
Abstract
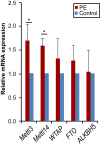
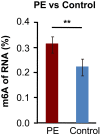
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent modification in eukaryotic mRNA and potential regulatory functions of m6A have been shown by mapping the RNA m6A modification landscape. m6A modification in active gene regulation manifests itself as altered methylation profiles. The number of reports regarding to the profiling of m6A modification and its potential role in the placenta of preeclampsia (PE) is small. In this work, placental samples were collected from PE and control patients. Expression of m6A-related genes was investigated using quantitative real-time PCR. MeRIP-seq and RNA-seq were performed to detect m6A methylation and mRNA expression profiles. Gene ontology (GO) functional and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were also conducted to explore the modified genes and their clinical significance. Our findings show that METTL3 and METTL14 were up-regulated in PE. In total, 685 m6A peaks were differentially expressed as determined by MeRIP-seq. Altered peaks of m6A-modified transcripts were primarily associated with nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of vascular-associated smooth muscle cell migration, and endoplasmic reticulum organisation. The m6A hyper-methylated genes of Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway, mTOR signalling pathway, and several cancer-related pathways may contribute to PE. We also verified that the significant increase of HSPA1A mRNA and protein expression was regulated by m6A modification, suggesting m6A plays a key role in the regulation of gene expression. Our data provide novel information regarding m6A modification alterations in PE and help our understanding of the pathogenesis of PE.
Keywords: m6A; Preeclampsia; RNA methylation.
©2020 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Characteristics of N6-methyladenosine modification patterns in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 May 20;42(5):690-697. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.05.09. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35673912 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Transcriptome-wide methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing profiling reveals m6A modification involved in response to heat stress in Apostichopus japonicus.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 11;25(1):1071. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10972-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39528936 Free PMC article.
-
The alteration of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification at the transcriptome-wide level in response of heat stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells.BMC Genomics. 2022 Dec 14;23(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-09067-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36517742 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of m6A modification in the great obstetrical syndromes.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(2):2234541. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2023.2234541. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023. PMID: 37474299 Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in Preeclampsia.Reprod Sci. 2023 Nov;30(11):3144-3152. doi: 10.1007/s43032-023-01250-8. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 37286755 Review.
Cited by
-
Pregnancy exposure to phthalates and DNA methylation in male placenta - An epigenome-wide association study.Environ Int. 2022 Feb;160:107054. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.107054. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Environ Int. 2022. PMID: 35032864 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profiling of N7-Methylguanosine Modification of Messenger RNA in Drug-Resistant Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 5;12:926296. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.926296. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35865472 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3-Mediated m6A RNA Methylation of ZBTB4 Interferes With Trophoblast Invasion and Maybe Involved in RSA.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 14;10:894810. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.894810. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35774226 Free PMC article.
-
Demethylase FTO-mediated m6A modification of SIK1 modulates placental cytotrophoblast syncytialization in type 2 diabetes mellitus.iScience. 2024 May 4;27(6):109900. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109900. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38883837 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis combined with clinical sample screening reveals that leptin may be a biomarker of preeclampsia.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1031950. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1031950. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36685185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonnet F, Roussel R, Natali A, Cauchi S, Petrie J, Laville M, Yengo L, Froguel P, Lange C, Lantieri O, Marre M, Balkau B, Ferrannini E. Parental history of type 2 diabetes, TCF7L2 variant and lower insulin secretion are associated with incident hypertension. Data from the DESIR and RISC cohorts. Diabetologia. 2013;56:2414–2423. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-3021-y. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

