A Structurally Novel Lipoyl Synthase in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis
- PMID: 32978128
- PMCID: PMC7657641
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01359-20
A Structurally Novel Lipoyl Synthase in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis
Abstract
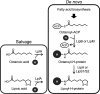
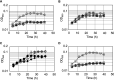
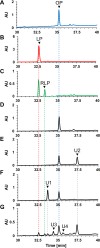
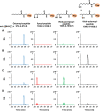
Lipoic acid is a sulfur-containing cofactor and a component of the glycine cleavage system (GCS) involved in C1 compound metabolism and the 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases that catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of 2-oxoacids. Lipoic acid is found in all domains of life and is generally synthesized as a lipoyl group on the H-protein of the GCS or the E2 subunit of 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases. Lipoyl synthase catalyzes the insertion of two sulfur atoms to the C-6 and C-8 carbon atoms of the octanoyl moiety on the octanoyl-H-protein or octanoyl-E2 subunit. Although the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis seemed able to synthesize lipoic acid, a classical lipoyl synthase (LipA) gene homolog cannot be found on the genome. In this study, we aimed to identify the lipoyl synthase in this organism. Genome information analysis suggested that the TK2109 and TK2248 genes, which had been annotated as biotin synthase (BioB), are both involved in lipoic acid metabolism. Based on the chemical reaction catalyzed by BioB, we predicted that the genes encode proteins that catalyze the lipoyl synthase reaction. Genetic analysis of TK2109 and TK2248 provided evidence that these genes are involved in lipoic acid biosynthesis. The purified TK2109 and TK2248 recombinant proteins exhibited lipoyl synthase activity toward a chemically synthesized octanoyl-octapeptide. These in vivo and in vitro analyses indicated that the TK2109 and TK2248 genes encode a structurally novel lipoyl synthase. TK2109 and TK2248 homologs are widely distributed among the archaeal genomes, suggesting that in addition to the LipA homologs, the two proteins represent a new group of lipoyl synthases in archaea.IMPORTANCE Lipoic acid is an essential cofactor for GCS and 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases, and α-lipoic acid has been utilized as a medicine and attracted attention as a supplement due to its antioxidant activity. The biosynthesis pathways of lipoic acid have been established in Bacteria and Eucarya but not in Archaea Although some archaeal species, including Sulfolobus, possess a classical lipoyl synthase (LipA) gene homolog, many archaeal species, including T. kodakarensis, do not. In addition, the biosynthesis mechanism of the octanoyl moiety, a precursor for lipoyl group biosynthesis, is also unknown for many archaea. As the enzyme identified in T. kodakarensis most likely represents a new group of lipoyl synthases in Archaea, the results obtained in this study provide an important step in understanding how lipoic acid is synthesized in this domain and how the two structurally distinct lipoyl synthases evolved in nature.
Keywords: Archaea; Thermococcus; biosynthesis; cofactor; hyperthermophile; lipoic acid; lipoyl synthase; metabolism.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Lipoate-Protein Ligase Is Required for De Novo Lipoyl-Protein Biosynthesis in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jul 12;88(13):e0064422. doi: 10.1128/aem.00644-22. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35736229 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Dephospho-Coenzyme A (Dephospho-CoA) Kinase in Thermococcus kodakarensis and Elucidation of the Entire CoA Biosynthesis Pathway in Archaea.mBio. 2019 Jul 23;10(4):e01146-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01146-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31337720 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic investigations of lipoic acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: both sulfur atoms in lipoic acid are contributed by the same lipoyl synthase polypeptide.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Mar 9;127(9):2860-1. doi: 10.1021/ja042428u. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 15740115
-
Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014 Jul;37(4):553-63. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9705-8. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014. PMID: 24777537 Review.
-
Assembly of Lipoic Acid on Its Cognate Enzymes: an Extraordinary and Essential Biosynthetic Pathway.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Apr 13;80(2):429-50. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00073-15. Print 2016 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27074917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipoic acid attachment to proteins: stimulating new developments.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Jun 27;88(2):e0000524. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00005-24. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38624243 Review.
-
Removal of phosphoglycolate in hyperthermophilic archaea.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 16;121(16):e2311390121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2311390121. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38593075 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel lipoic acid biosynthesis pathway reveals the complex evolution of lipoate assembly in prokaryotes.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jun 27;21(6):e3002177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002177. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37368881 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of LipS1 and LipS2 from Thermococcus kodakarensis: Proteins Annotated as Biotin Synthases, which Together Catalyze Formation of the Lipoyl Cofactor.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2022 Oct 19;2(5):509-520. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00018. Epub 2022 Jul 14. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2022. PMID: 36281299 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Enzymatic Analysis of an Archaeal ATP-Dependent Serine Kinase from the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Staphylothermus marinus.J Bacteriol. 2021 Jul 22;203(16):e0002521. doi: 10.1128/JB.00025-21. Epub 2021 Jul 22. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34096778 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

