Nimotuzumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy versus platinum-based chemotherapy alone in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 32973932
- PMCID: PMC7498835
- DOI: 10.1177/1758835920953738
Nimotuzumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy versus platinum-based chemotherapy alone in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Palliative chemotherapy has been the mainstay treatment for patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (R/M-NPC). However, little is known about the efficacy and toxicity of nimotuzumab (NTZ) - a monoclonal antibody drug targeting epidermal growth factor receptor - plus chemotherapy (CT) versus CT alone for these patients.
Methods: The database at Cancer Hospital of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences was queried for patients diagnosed with NPC who received CT with or without NTZ between 2004 and 2018. Treatment compliance, survival outcomes, and adverse effects were compared among these groups.
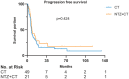
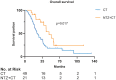
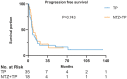
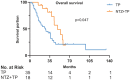
Results: Records of 70 patients with R/M-NPC were reviewed: 21 (30%) received NTZ plus CT (NTZ+CT) and 49 (70%) received CT. CT regimens included gemcitabine plus platinum, taxane plus platinum (TP), and fluorouracil plus platinum. Comparing the CT group with NTZ+CT group, the median follow up was 62 months (range = 3-133) versus 59 months (range = 9-117); median progression free survival was 7.5 [95% confidence interval (CI) 6.552-8.381] months versus 8.5 (95% CI 6.091-10.976) months, p = 0.424; median overall survival (OS) was 25.6 (95% CI 18.888-32.379) months versus 48.6 (95% CI 35.619-61.581) months, p = 0.017, respectively. Multivariable analysis established treatment group (CT versus NTZ+CT) as an independent prognostic factor for OS (hazard ratio, 0.5; 95% CI 0.255-0.979; p = 0.043). No significant difference with regard to toxicities was observed between the two groups. Among them, a subgroup analysis was performed in 53 (75.7%) patients who received TP with or without NTZ, which showed similar results.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that NTZ+CT provides a novel treatment option and prolongs survival significantly for R/M-NPC.
Keywords: adverse effects; chemotherapy; distant metastasis; efficacy; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; nimotuzumab; recurrence.
© The Author(s), 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Precision drugs for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2023 Nov 3;26(6):585. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12284. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 38023360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy with or without Anti-EGFR-Targeted Treatment for Stage II-IVb Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Retrospective Analysis with a Large Cohort and Long Follow-up.Theranostics. 2017 Jun 1;7(8):2314-2324. doi: 10.7150/thno.19710. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28740554 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment and Survival Outcomes Associated With Platinum Plus Low-Dose, Long-term Fluorouracil for Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2138444. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.38444. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34902036 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab or nimotuzumab plus intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus cisplatin plus intensity-modulated radiotherapy for stage II-IVb nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2017 Sep 15;141(6):1265-1276. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30819. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28577306
-
Induction chemotherapy plus concomitant chemoradiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An updated network meta-analysis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021 Apr;160:103244. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103244. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33582249 Review.
Cited by
-
Leptomeningeal metastasis from de novo metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a case report.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Sep;11(9):3349-3356. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-1211. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36237253 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab or nimotuzumab in combination with chemotherapy for treating recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta‑analysis and systemic review.Oncol Lett. 2023 Apr 5;25(5):204. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13790. eCollection 2023 May. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37123019 Free PMC article.
-
Precision drugs for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2023 Nov 3;26(6):585. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12284. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 38023360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Sequential Challenge.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;14(17):4111. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174111. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone: efficacy and prognostic analysis in recurrent metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2622-2632. doi: 10.62347/PAAP2909. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39006268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 68: 394–424. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 115–132. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT, et al. Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current practice and future perspective. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 3356–3364. - PubMed
-
- Tan EH, Khoo KS, Wee J, et al. Phase II trial of a paclitaxel and carboplatin combination in Asian patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Oncol 1999; 10: 235–237. - PubMed
-
- Ngan RK, Yiu HH, Lau WH, et al. Combination gemcitabine and cisplatin chemotherapy for metastatic or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: report of a phase II study. Ann Oncol 2002; 13: 1252–1258. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

