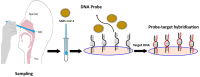
Future developments in biosensors for field-ready SARS-CoV-2 virus diagnostics
- PMID: 32970352
- PMCID: PMC7537309
- DOI: 10.1002/bab.2033
Future developments in biosensors for field-ready SARS-CoV-2 virus diagnostics
Abstract
According to the evidence, the coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is caused by a zoonotic pathogen named respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This virus can spread through personal contact, respiratory droplets, and also through airborne transmission. A rapid, low-cost, and effective biosensor platform is essential to diagnose patients with COVID-19 infection, predominantly the asymptomatic individuals, and prevent the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 via transmission routes. The objective of this review is to provide a comparative view among current diagnostic methods, focusing on recently suggested biosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV2 in clinical samples. A capable SARS-CoV-2 biosensor can be designed by the holistic insights of various biosensor studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; biosensor; coronavirus; real-time PCR; serological assays.
© 2020 International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biosensors as a future diagnostic approach for COVID-19.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119117. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119117. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33508293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Utility of Biosensing Platforms for Confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 May 24;11(6):167. doi: 10.3390/bios11060167. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 26;188(6):199. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34041585 Free PMC article.
-
The potential application of electrochemical biosensors in the COVID-19 pandemic: A perspective on the rapid diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Mar 15;176:112905. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112905. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33358285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological characteristics and biomarkers of novel SARS-CoV-2 facilitated rapid development and implementation of diagnostic tools and surveillance measures.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Apr 1;177:112969. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.112969. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33434780 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Worldwide prevalence of fungal coinfections among COVID-19 patients: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022 Feb;13(1):15-23. doi: 10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0293. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022. PMID: 35255675 Free PMC article.
-
Internet of Things Concept in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multi-Sensor Application Design.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 10;22(2):503. doi: 10.3390/s22020503. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062463 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Bacterial and Fungal Human Respiratory Microbiota in COVID-19 Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 23;2021:6670798. doi: 10.1155/2021/6670798. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33681368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Portable Tools for COVID-19 Point-of-Care Detection: A Review.IEEE Sens J. 2021 Sep 7;21(21):23737-23750. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3110857. eCollection 2021 Nov 1. IEEE Sens J. 2021. PMID: 35582343 Free PMC article.
-
3D simulation of microfluidic biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 S protein binding kinetics using new reaction surface design.Eur Phys J Plus. 2022;137(2):241. doi: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02470-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Eur Phys J Plus. 2022. PMID: 35194535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fani, M. , Teimoori, A. , and Ghafari, S. (2020) Future Virol.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous