DNA binding activity of the proximal C-terminal domain of rat DNA topoisomerase IIβ is involved in ICRF-193-induced closed-clamp formation
- PMID: 32960919
- PMCID: PMC7508362
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239466
DNA binding activity of the proximal C-terminal domain of rat DNA topoisomerase IIβ is involved in ICRF-193-induced closed-clamp formation
Abstract
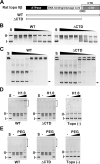
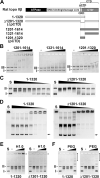
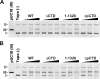
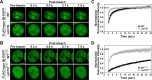
DNA topoisomerase II (topo II) is an essential enzyme that regulates DNA topology by DNA cleavage and re-ligation. In vertebrates, there are two isozymes, α and β. The C-terminal domain (CTD) of the isozymes, which shows a low degree of sequence homology between α and β, is involved in each isozyme-specific intracellular behavior. The CTD of topo IIβ is supposedly involved in topo II regulation. Topo IIβ is maintained in an inactive state in the nucleoli by the binding of RNA to the 50-residue region termed C-terminal regulatory domain (CRD) present in the CTD. Although in vitro biochemical analysis indicates that the CTD of topo IIβ has DNA binding activity, it is unclear whether CTD influences catalytic reaction in the nucleoplasm. Here, we show that the proximal CTD (hereafter referred to as pCTD) of rat topo IIβ, including the CRD, is involved in the catalytic reaction in the nucleoplasm. We identified the pCTD as a domain with DNA binding activity by in vitro catenation assay and electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Fluorescence recovery after photo-bleaching (FRAP) analysis of pCTD-lacking mutant (ΔpCTD) showed higher mobility in nucleoplasm than that of the wild-type enzyme, indicating that the pCTD also affected the nuclear dynamics of topo IIβ. ICRF-193, one of the topo II catalytic inhibitors, induces the formation of closed-clamp intermediates of topo II. Treatment of ΔpCTD with ICRF-193 significantly decreased the efficiency of closed-clamp formation. Altogether, our data indicate that the binding of topo IIβ to DNA through the pCTD is required for the catalytic reaction in the nucleoplasm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of catalytic activity and nucleolar localization of rat DNA topoisomerase IIα through its C-terminal domain.Genes Genet Syst. 2021 Mar 23;95(6):291-302. doi: 10.1266/ggs.20-00038. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Genes Genet Syst. 2021. PMID: 33551432
-
Nuclear dynamics of topoisomerase IIβ reflects its catalytic activity that is regulated by binding of RNA to the C-terminal domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Aug;42(14):9005-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku640. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25034690 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the C-terminal domains of topoisomerase IIα and topoisomerase IIβ in regulation of the decatenation checkpoint.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):5995-6010. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx325. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28472494 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of DNA Topoisomerase IIβ in Transcription.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 29;19(7):1917. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071917. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29966298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The function of DNA topoisomerase IIβ in neuronal development.Neurosci Bull. 2010 Oct;26(5):411-6. doi: 10.1007/s12264-010-0625-9. Neurosci Bull. 2010. PMID: 20882068 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolar translocation of human DNA topoisomerase II by ATP depletion and its disruption by the RNA polymerase I inhibitor BMH-21.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 2;11(1):21533. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00958-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34728715 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-associated H58Y mutation affects the nuclear dynamics of human DNA topoisomerase IIβ.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 30;12(1):20627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24883-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36450898 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

