Pioneer of prostate cancer: past, present and the future of FOXA1
- PMID: 32946061
- PMCID: PMC7815845
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00786-8
Pioneer of prostate cancer: past, present and the future of FOXA1
Abstract
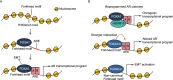
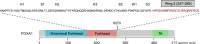
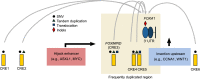
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed non-cutaneous cancers in North American men. While androgen deprivation has remained as the cornerstone of prostate cancer treatment, resistance ensues leading to lethal disease. Forkhead box A1 (FOXA1) encodes a pioneer factor that induces open chromatin conformation to allow the binding of other transcription factors. Through direct interactions with the Androgen Receptor (AR), FOXA1 helps to shape AR signaling that drives the growth and survival of normal prostate and prostate cancer cells. FOXA1 also possesses an AR-independent role of regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In prostate cancer, mutations converge onto the coding sequence and cis-regulatory elements (CREs) of FOXA1, leading to functional alterations. In addition, FOXA1 activity in prostate cancer can be modulated post-translationally through various mechanisms such as LSD1-mediated protein demethylation. In this review, we describe the latest discoveries related to the function and regulation of FOXA1 in prostate cancer, pointing to their relevance to guide future clinical interventions.
Keywords: FOXA1; epigenetics; pioneer factor; prostate cancer; transcription factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromatin binding of FOXA1 is promoted by LSD1-mediated demethylation in prostate cancer.Nat Genet. 2020 Oct;52(10):1011-1017. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0681-7. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Nat Genet. 2020. PMID: 32868907 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor-independent function of FoxA1 in prostate cancer metastasis.Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 15;73(12):3725-36. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3468. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23539448 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct structural classes of activating FOXA1 alterations in advanced prostate cancer.Nature. 2019 Jul;571(7765):413-418. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1347-4. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31243372 Free PMC article.
-
FOXA1: a transcription factor with parallel functions in development and cancer.Biosci Rep. 2012 Apr 1;32(2):113-30. doi: 10.1042/BSR20110046. Biosci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22115363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaping Chromatin States in Prostate Cancer by Pioneer Transcription Factors.Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 15;80(12):2427-2436. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3447. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32094298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-tiered chemical proteomic maps of tryptoline acrylamide-protein interactions in cancer cells.Nat Chem. 2024 Oct;16(10):1592-1604. doi: 10.1038/s41557-024-01601-1. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Nat Chem. 2024. PMID: 39138346 Free PMC article.
-
Development of gemcitabine-modified miRNA mimics as cancer therapeutics for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Jan 26;32(1):200769. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200769. eCollection 2024 Mar 21. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38596306 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the epigenetics and chromatin loop dynamics of androgen receptor-mediated transcription.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 3;15(1):9494. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53758-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39489778 Free PMC article.
-
Positive epigenetic regulation loop between AR and NSUN2 promotes prostate cancer progression.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Sep;12(9):e1028. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1028. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36169095 Free PMC article.
-
FOXA1 prevents nutrients deprivation induced autophagic cell death through inducing loss of imprinting of IGF2 in lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Aug 16;13(8):711. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05150-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35974000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society (2019) Cancer Facts & Figures 2019
-
- Arrowsmith CH, Bountra C, Fish PV, Lee K, Schapira M. Epigenetic protein families: a new frontier for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:384–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

