Redox signaling and Alzheimer's disease: from pathomechanism insights to biomarker discovery and therapy strategy
- PMID: 32944245
- PMCID: PMC7488504
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-020-00218-z
Redox signaling and Alzheimer's disease: from pathomechanism insights to biomarker discovery and therapy strategy
Abstract
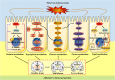
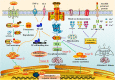
Abstract: Aging and average life expectancy have been increasing at a rapid rate, while there is an exponential risk to suffer from brain-related frailties and neurodegenerative diseases as the population ages. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide with a projected expectation to blossom into the major challenge in elders and the cases are forecasted to increase about 3-fold in the next 40 years. Considering the etiological factors of AD are too complex to be completely understood, there is almost no effective cure to date, suggesting deeper pathomechanism insights are urgently needed. Metabolites are able to reflect the dynamic processes that are in progress or have happened, and metabolomic may therefore provide a more cost-effective and productive route to disease intervention, especially in the arena for pathomechanism exploration and new biomarker identification. In this review, we primarily focused on how redox signaling was involved in AD-related pathologies and the association between redox signaling and altered metabolic pathways. Moreover, we also expatiated the main redox signaling-associated mechanisms and their cross-talk that may be amenable to mechanism-based therapies. Five natural products with promising efficacy on AD inhibition and the benefit of AD intervention on its complications were highlighted as well.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Inflammation; Metabolomics; Neurodegenerative disease; Oxidative stress.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolomics in renal cell carcinoma: From biomarker identification to pathomechanism insights.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Nov 30;695:108623. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108623. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 33039388 Review.
-
The Triangle of Death in Alzheimer's Disease Brain: The Aberrant Cross-Talk Among Energy Metabolism, Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling, and Protein Homeostasis Revealed by Redox Proteomics.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Mar 10;26(8):364-387. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6759. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27626216 Review.
-
Decoding the Role of Astrocytes in the Entorhinal Cortex in Alzheimer's Disease Using High-Dimensional Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing Data and Next-Generation Knowledge Discovery Methodologies: Focus on Drugs and Natural Product Remedies for Dementia.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 28;12:720170. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.720170. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35295737 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic-guided discovery of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers from body fluid.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Oct;95(10):2005-2024. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24048. Epub 2017 Mar 16. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 28301062 Review.
-
Characterizing Alzheimer's disease through metabolomics and investigating anti-Alzheimer's disease effects of natural products.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Jun;1398(1):130-141. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13385. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28632966 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox signaling and metabolism in Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Nov 3;14:1003721. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1003721. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36408110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox dysregulation as a driver for DNA damage and its relationship to neurodegenerative diseases.Transl Neurodegener. 2023 Apr 14;12(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40035-023-00350-4. Transl Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 37055865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hindlimb immobilization induces insulin resistance and elevates mitochondrial ROS production in the hippocampus of female rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2024 Sep 1;137(3):512-526. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00234.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 4. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2024. PMID: 38961821
-
Bioinformatic analysis of hippocampal histopathology in Alzheimer's disease and the therapeutic effects of active components of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 16;15:1424803. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1424803. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39221152 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of programmed cell death-related lncRNAs in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.Apoptosis. 2024 Oct;29(9-10):1584-1599. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01984-z. Epub 2024 Jun 9. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38853201
References
-
- Nakamura A, Kaneko N, Villemagne VL, et al. High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2018;554(7691):249–254. - PubMed
-
- Cuperlovic-Culf M, Badhwar A. Recent advances from metabolomics and lipidomics application in Alzheimer's disease inspiring drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020;15(3):319–331. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

