Engineered Extracellular Vesicles: Tailored-Made Nanomaterials for Medical Applications
- PMID: 32942556
- PMCID: PMC7558114
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10091838
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles: Tailored-Made Nanomaterials for Medical Applications
Abstract
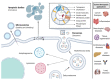
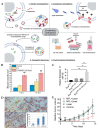
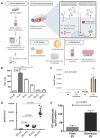
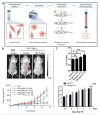
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as promising nanoscale therapeutics due to their intrinsic role as mediators of intercellular communication, regulating tissue development and homeostasis. The low immunogenicity and natural cell-targeting capabilities of EVs has led to extensive research investigating their potential as novel acellular tools for tissue regeneration or for the diagnosis of pathological conditions. However, the clinical use of EVs has been hindered by issues with yield and heterogeneity. From the modification of parental cells and naturally-derived vesicles to the development of artificial biomimetic nanoparticles or the functionalisation of biomaterials, a multitude of techniques have been employed to augment EVs therapeutic efficacy. This review will explore various engineering strategies that could promote EVs scalability and therapeutic effectiveness beyond their native utility. Herein, we highlight the current state-of-the-art EV-engineering techniques with discussion of opportunities and obstacles for each. This is synthesised into a guide for selecting a suitable strategy to maximise the potential efficacy of EVs as nanoscale therapeutics.
Keywords: EV engineering; EV-functionalised biomaterials; artificial EVs; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; microvesicles; nanomedicine; regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioengineering extracellular vesicles: smart nanomaterials for bone regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Apr 27;21(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01895-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37106449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles for Immunomodulation in Tissue Regeneration.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022 Aug;28(8):393-404. doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2022.0000059. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022. PMID: 35856810 Review.
-
Functional Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Medicine.Small. 2022 Sep;18(36):e2106569. doi: 10.1002/smll.202106569. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Small. 2022. PMID: 35322545 Review.
-
The Emerging Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Cell-Free Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021 Oct;27(5):530-538. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0222. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021. PMID: 33126845 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Tissue Engineering: Biology and Engineered Strategy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2022 Nov;11(21):e2201384. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202201384. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022. PMID: 36053562 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome for mRNA delivery: strategies and therapeutic applications.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 4;22(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02634-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38965553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemically Modified Extracellular Vesicles and Applications in Radiolabeling and Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 16;14(3):653. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030653. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35336027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Musculoskeletal Regeneration: Modulating the Therapy of the Future.Cells. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):43. doi: 10.3390/cells11010043. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR delivery with extracellular vesicles: Promises and challenges.J Extracell Biol. 2023 Sep 21;2(9):e111. doi: 10.1002/jex2.111. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Extracell Biol. 2023. PMID: 38938376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cell-Based Acellular Therapy: Insight into Biogenesis, Bioengineering and Therapeutic Applications of Exosomes.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 3;14(7):792. doi: 10.3390/biom14070792. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

