Dendrimers and Dendritic Materials: From Laboratory to Medical Practice in Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 32937793
- PMCID: PMC7560085
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12090874
Dendrimers and Dendritic Materials: From Laboratory to Medical Practice in Infectious Diseases
Abstract
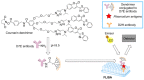
Infectious diseases are one of the main global public health risks, predominantly caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. The control of infections is founded on three main pillars: prevention, treatment, and diagnosis. However, the appearance of microbial resistance has challenged traditional strategies and demands new approaches. Dendrimers are a type of polymeric nanoparticles whose nanometric size, multivalency, biocompatibility, and structural perfection offer boundless possibilities in multiple biomedical applications. This review provides the reader a general overview about the uses of dendrimers and dendritic materials in the treatment, prevention, and diagnosis of highly prevalent infectious diseases, and their advantages compared to traditional approaches. Examples of dendrimers as antimicrobial agents per se, as nanocarriers of antimicrobial drugs, as well as their uses in gene transfection, in vaccines or as contrast agents in imaging assays are presented. Despite the need to address some challenges in order to be used in the clinic, dendritic materials appear as an innovative tool with a brilliant future ahead in the clinical management of infectious diseases and many other health issues.
Keywords: amoeba; bacteria; dendrimer; fungi; infection; nanoparticle; parasite; prion; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
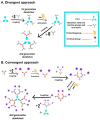
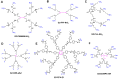
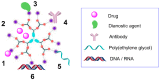
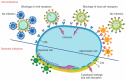

Similar articles
-
Prevention of microbial biofilms - the contribution of micro and nanostructured materials.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(29):3311. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140304101314. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24606506
-
Tuberculosis.In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. PMID: 30212088 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Recent progress in dendrimer-based nanomedicine development.Arch Pharm Res. 2018 Jun;41(6):571-582. doi: 10.1007/s12272-018-1008-4. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Arch Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29450862 Review.
-
Dendrimers--revolutionary drugs for infectious diseases.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2012 Sep-Oct;4(5):469-91. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1181. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22761054 Review.
-
Dendrimer-based nanocarriers: a versatile platform for drug delivery.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017 Jan;9(1). doi: 10.1002/wnan.1409. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27126551 Review.
Cited by
-
The Combination of Antibiotic and Non-Antibiotic Compounds Improves Antibiotic Efficacy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15493. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015493. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functionalized Dendrimer Platforms as a New Forefront Arsenal Targeting SARS-CoV-2: An Opportunity.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 18;13(9):1513. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091513. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eradication of Candida albicans Biofilm Viability: In Vitro Combination Therapy of Cationic Carbosilane Dendrons Derived from 4-Phenylbutyric Acid with AgNO3 and EDTA.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jul 18;7(7):574. doi: 10.3390/jof7070574. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356953 Free PMC article.
-
Insight on the Structure-to-Activity of Carbosilane Metallodendrimers in the Fight against Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 17;10(5):589. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050589. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067558 Free PMC article.
-
Trends on Novel Targets and Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Parkinson's disease: Recent Advancement in Drug Development.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(15):987-1011. doi: 10.2174/0113894501312703240826070530. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 39313872 Review.
References
-
- Zorrilla-Vaca A., Escandón-Vargas K. The importance of infection control and prevention in anesthesiology. Colomb. J. Anesthesiol. 2017;45:69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.rcae.2017.10.001. - DOI
-
- Martínez A.J. Las enfermedades infecciosas emergentes y reemergentes, un tema de interés para todos. Rev. Med. Electron. 2014;36:537–539.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

