Taste transduction and channel synapses in taste buds
- PMID: 32936320
- PMCID: PMC9386877
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-020-02464-4
Taste transduction and channel synapses in taste buds
Abstract
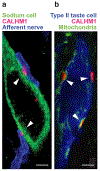
The variety of taste sensations, including sweet, umami, bitter, sour, and salty, arises from diverse taste cells, each of which expresses specific taste sensor molecules and associated components for downstream signal transduction cascades. Recent years have witnessed major advances in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying transduction of basic tastes in taste buds, including the identification of the bona fide sour sensor H+ channel OTOP1, and elucidation of transduction of the amiloride-sensitive component of salty taste (the taste of sodium) and the TAS1R-independent component of sweet taste (the taste of sugar). Studies have also discovered an unconventional chemical synapse termed "channel synapse" which employs an action potential-activated CALHM1/3 ion channel instead of exocytosis of synaptic vesicles as the conduit for neurotransmitter release that links taste cells to afferent neurons. New images of the channel synapse and determinations of the structures of CALHM channels have provided structural and functional insights into this unique synapse. In this review, we discuss the current view of taste transduction and neurotransmission with emphasis on recent advances in the field.
Keywords: CALHM; Ion channel; Sensory; Synapse; Taste.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

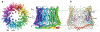
Similar articles
-
Signal transduction and information processing in mammalian taste buds.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Aug;454(5):759-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0247-x. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17468883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes.Nature. 2013 Mar 14;495(7440):223-6. doi: 10.1038/nature11906. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23467090 Free PMC article.
-
How do taste cells lacking synapses mediate neurotransmission? CALHM1, a voltage-gated ATP channel.Bioessays. 2013 Dec;35(12):1111-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300077. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 24105910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
All-Electrical Ca2+-Independent Signal Transduction Mediates Attractive Sodium Taste in Taste Buds.Neuron. 2020 Jun 3;106(5):816-829.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.03.006. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32229307
-
Taste Bud Connectome: Implications for Taste Information Processing.J Neurosci. 2022 Feb 2;42(5):804-816. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0838-21.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 7. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34876471 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contribution of TRPC3-mediated Ca2+ entry to taste transduction.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Aug;475(8):1009-1024. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02834-8. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 37369785
-
Recent Advances in Artificial Sensory Neurons: Biological Fundamentals, Devices, Applications, and Challenges.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Nov 13;17(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01550-x. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 39537845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taste alterations in patients following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A qualitative study.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2023 Oct 9;10(12):100311. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2023.100311. eCollection 2023 Dec. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2023. PMID: 38033392 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding of calmodulin to the cytosolic C-terminal regions of sweet/umami taste receptors.J Biochem. 2023 Oct 31;174(5):451-459. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvad060. J Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37527916 Free PMC article.
-
Taste Cells of the Type III Employ CASR to Maintain Steady Serotonin Exocytosis at Variable Ca2+ in the Extracellular Medium.Cells. 2022 Apr 18;11(8):1369. doi: 10.3390/cells11081369. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2000) A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell 100:693–702 - PubMed
-
- Anand KK, Zuniga JR (1997) Effect of amiloride on suprathreshold NaCl, LiCl, and KCl salt taste in humans. Physiol Behav 62:925–929 - PubMed
-
- Bigiani A (2017) Calcium homeostasis modulator 1-like currents in rat fungiform taste cells expressing amiloride-sensitive sodium currents. Chem Senses 42:343–359 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

