Monascin accelerates anoikis in circulating tumor cells and prevents breast cancer metastasis
- PMID: 32934733
- PMCID: PMC7471737
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12029
Monascin accelerates anoikis in circulating tumor cells and prevents breast cancer metastasis
Abstract
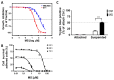
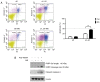
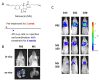
Anoikis resistance has been observed in various types of cancers in which anchorage-independent growth is a crucial step for cancer metastasis. Therefore, agents interfering with this specific cancer cell behavior may be integrated into novel antimetastatic strategies. Monascin (MS), a secondary metabolite found in Monascus species, is a known potent chemopreventive compound used for treating metabolic complications; however, the effect of MS on anoikis resistance has not been investigated. In this study, 4T1 breast cells were treated with MS under either suspension or adhesion conditions. The higher cytotoxicity of MS was more potent against suspended cells than against adherent cells. This selective cytotoxicity was due to the induction of anoikis, which was evidenced by changes in cell aggregation, caspase activity, and Annexin V/propidium iodide binding as well as the results of systemic metastasis in an animal model. Furthermore, MS inhibited E-cadherin and β-catenin expression in the cells; the treated cells formed spherical aggregates, which suggested that anchorage-independent growth was prevented by MS. These results provide new insights into the mechanisms underlying the growth-preventing effect of MS on cancer cells and indicate the potential ability of MS to suppress metastasis.
Keywords: anoikis; circulating tumor cell; metastasis; monascin.
Copyright: © Chen et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The chemopreventive isothiocyanate sulforaphane reduces anoikis resistance and anchorage-independent growth in non-small cell human lung cancer cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 1;362:116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.10.020. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30365975
-
E-cadherin cell-cell adhesion in ewing tumor cells mediates suppression of anoikis through activation of the ErbB4 tyrosine kinase.Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 1;67(7):3094-105. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3259. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17409416 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Profiles Associated with Anoikis Resistance of Metastatic MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(2):581-90. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2016.17.2.581. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016. PMID: 26925647
-
Anoikis: a necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 1;76(11):1352-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.023. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18708031 Review.
-
Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1833(12):3481-3498. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23830918 Review.
Cited by
-
Anoikis resistance--protagonists of breast cancer cells survive and metastasize after ECM detachment.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Aug 3;21(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01183-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37537585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastasis and MAPK Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3847. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073847. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel risk model based on anoikis: Predicting prognosis and immune infiltration in cutaneous melanoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 16;13:1090857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1090857. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36726781 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Increase the Natural Killer Resistance of Circulating Tumor Cells via Intercellular Signaling of cGAS-STING-IFNβ-HLA.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(21):e2400888. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400888. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38638003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sirimangkalakitti N, Chamni S, Suwanborirux K, Chanvorachote P. Renieramycin M Sensitizes Anoikis-resistant H460 lung cancer cells to anoikis. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1665–1671. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
