Effects of quercetin-conjugated with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on learning and memory improvement through targeting microRNAs/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 32934245
- PMCID: PMC7493930
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71678-4
Effects of quercetin-conjugated with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on learning and memory improvement through targeting microRNAs/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
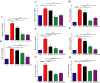
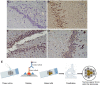
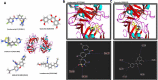
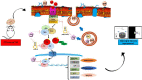
Quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (QCSPIONs) have an ameliorative effect on diabetes-induced memory impairment. The current study aimed to compare the effect of quercetin (QC) and QCSPIONs on inflammation-related microRNAs and NF-κB signaling pathways in the hippocampus of diabetic rats. The expression levels of miR-146a, miR-9, NF-κB, and NF-κB-related downstream genes, including TNF-α, BACE1, AβPP, Bax, and Bcl-2 were measured using quantitative real-time PCR. To determine the NF-κB activity, immunohistochemical expression of NF-κB/p65 phosphorylation was employed. Computer simulated docking analysis also performed to find the QC target proteins involved in the NF-κB pathway. Results indicate that diabetes significantly upregulated the expression levels of miR-146a, miR-9, TNF-α, NF-κB, and subsequently AβPP, BACE1, and Bax. Expression analysis shows that QCSPIONs are more effective than pure QC in reducing the expression of miR-9. Interestingly, QCSPIONs reduce the pathological activity of NF-κB and subsequently normalize BACE1, AβPP, and the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 expression better than pure QC. Comparative docking analyses also show the stronger binding affinity of QC to IKK and BACE1 proteins compared to specific inhibitors of each protein. In conclusion, our study suggests the potent efficacy of QCSPIONs as a promising drug delivery system in memory improvement through targeting the NF-κB pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quercetin attenuates neurotoxicity induced by iron oxide nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Oct 18;19(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01059-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34663344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In diabetic male Wistar rats, quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have an effect on the SIRT1/p66Shc-mediated pathway related to cognitive impairment.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Dec 21;24(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00725-3. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38129872 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (QCSPIONs) increases Nrf2 expression via miR-27a mediation to prevent memory dysfunction in diabetic rats.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 29;10(1):15957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71971-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32994439 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 11;13:6311-6324. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S177871. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30349252 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin‑conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modulate glucose metabolism-related genes and miR-29 family in the hippocampus of diabetic rats.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 21;11(1):8618. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87687-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33883592 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quercetin attenuates neurotoxicity induced by iron oxide nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Oct 18;19(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01059-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34663344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotherapeutic effects of quercetin-loaded nanoparticles and Biochanin-A extracted from Trifolium alexandrinum on PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling in the cerebral cortex of male diabetic rats.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 29;19(4):e0301355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301355. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38683825 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Neuroprotective Role of Free and Encapsulated Quercetin Mediated by miRNA against Neurological Diseases.Nutrients. 2021 Apr 16;13(4):1318. doi: 10.3390/nu13041318. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33923599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects and Therapeutic Potential of the Citrus Flavonoid Hesperetin in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Nutrients. 2022 May 26;14(11):2228. doi: 10.3390/nu14112228. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35684025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In diabetic male Wistar rats, quercetin-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have an effect on the SIRT1/p66Shc-mediated pathway related to cognitive impairment.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Dec 21;24(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00725-3. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38129872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donaghue KC, et al. Microvascular and macrovascular complications in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes. 2014;15:257–269. - PubMed
-
- Guo J, et al. Impaired neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation in streptozotocin-induced and spontaneous diabetic mice. Neurosci. Res. 2010;68:329–336. - PubMed
-
- Sukhov I, Chistyakova O, Shipilov V, Doilnitsyn A, Shpakov A. Spatial memory and regulation of brain adenylyl cyclase by serotonin and dopamine in rat with streptozotocin diabetes. Rossiiskii fiziologicheskii zhurnal imeni IM Sechenova. 2015;101:279–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

