Downregulation of Cypher induces apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via Akt/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 32922198
- PMCID: PMC7484636
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.48872
Downregulation of Cypher induces apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via Akt/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
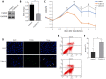
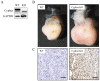
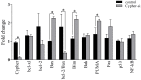
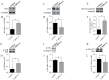
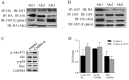
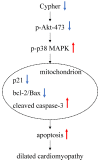
Background: Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is considered as the most common form of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy with a high mortality worldwide. Cytoskeleton protein Cypher plays an important role in maintaining cardiac function. Genetic studies in human and animal models revealed that Cypher is involved in the development of DCM. However, the underlying molecular mechanism is not fully understood. Accumulating evidences suggest that apoptosis in myocytes may contribute to DCM. Thus, the purpose of this study is to define whether lack of Cypher in cardiomyocytes can elevate apoptosis signaling and lead to DCM eventually. Methods and Results: Cypher-siRNA sufficiently inhibited Cypher expression in cardiomyocytes. TUNEL-positive cardiomyocytes were increased in both Cypher knockdown neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and Cypher knockout mice hearts, which were rare in the control group. Flow cytometry further confirmed that downregulation of Cypher significantly increased myocytes apoptosis in vitro. Cell counting kit-8 assay revealed that Cypher knockdown in H9c2 cells significantly reduced cell viability. Cypher knockdown was found to increase cleaved caspase-3 expression and suppress p21, ratio of bcl-2 to Bax. Cypher-deficiency induced apoptosis was linked to downregulation of Akt activation and elevated p-p38 MAPK accumulation. Pharmacological activation of Akt with SC79 attenuated apoptosis with enhanced phosphorylation of Akt and reduced p-p38 MAPK and Bax expression. Conclusions: Downregulation of Cypher participates in the promotion of cardiomyocytes apoptosis through inhibiting Akt dependent pathway and enhancing p38 MAPK phosphorylation. These findings may provide a new potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of DCM.
Keywords: Akt; Cypher; apoptosis; dilated cardiomyopathy; p38 MAPK.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cypher/ZASP is a novel A-kinase anchoring protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29403-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470708. Epub 2013 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23996002 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac-specific ablation of Cypher leads to a severe form of dilated cardiomyopathy with premature death.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Feb 15;18(4):701-13. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn400. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19028670 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 induces apoptosis in hippocampus through downregulating PI3K/Akt and upregulating p38 MAPK signaling pathways.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jun 4;6(6):e1775. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.146. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26043075 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc homeostasis plays an important role in the prevention of obesity-induced cardiac inflammation, remodeling and dysfunction.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Dec;62:126615. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126615. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32683230 Review.
-
Advances in the role and mechanism of BAG3 in dilated cardiomyopathy.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Jan;26(1):183-194. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09899-7. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 31808029 Review.
Cited by
-
PDZ and LIM Domain-Encoding Genes: Their Role in Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;15(20):5042. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205042. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD47 antibody protects mice from doxorubicin-induced myocardial damage by suppressing cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):350. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11277. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35493436 Free PMC article.
-
Shengqiyichang decoction regulates antitumor immunity in colorectal cancer by downregulating lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D via the protein kinase B/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 9;10(21):e39071. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39071. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524806 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals Downstream PKA Effectors of AKAP Cypher/ZASP in the Pathogenesis of Dilated Cardiomyopathy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 13;8:753072. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.753072. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34966794 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular basis of cardiomyopathy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Feb 1;322(2):H181-H233. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00562.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34797172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lopez-Ayala JM, Ortiz-Genga M, Gomez-Milanes I, Lopez-Cuenca D, Ruiz-Espejo F, Sanchez-Munoz JJ. et al. A mutation in the Z-line Cypher/ZASP protein is associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Clin Genet. 2015;88(2):172–176. - PubMed
-
- Arimura T, Hayashi T, Terada H, Lee SY, Zhou Q, Takahashi M. et al. A Cypher/ZASP mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy alters the binding affinity to protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(8):6746–6752. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

