Glycerophosphodiesterase 3 (GDE3) is a lysophosphatidylinositol-specific ectophospholipase C acting as an endocannabinoid signaling switch
- PMID: 32917725
- PMCID: PMC7667972
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015278
Glycerophosphodiesterase 3 (GDE3) is a lysophosphatidylinositol-specific ectophospholipase C acting as an endocannabinoid signaling switch
Abstract
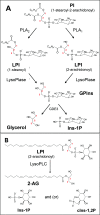
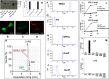
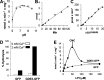
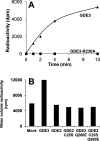
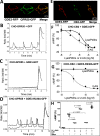
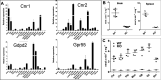
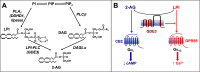
Endocannabinoid signaling plays a regulatory role in various (neuro)biological functions. 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is the most abundant endocannabinoid, and although its canonical biosynthetic pathway involving phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C and diacylglycerol lipase α is known, alternative pathways remain unsettled. Here, we characterize a noncanonical pathway implicating glycerophosphodiesterase 3 (GDE3, from GDPD2 gene). Human GDE3 expressed in HEK293T cell membranes catalyzed the conversion of lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) into monoacylglycerol and inositol-1-phosphate. The enzyme was equally active against 1-acyl and 2-acyl LPI. When using 2-acyl LPI, where arachidonic acid is the predominant fatty acid, LC-MS analysis identified 2-AG as the main product of LPI hydrolysis by GDE3. Furthermore, inositol-1-phosphate release into the medium occurred upon addition of LPI to intact cells, suggesting that GDE3 is actually an ecto-lysophospholipase C. In cells expressing G-protein-coupled receptor GPR55, GDE3 abolished 1-acyl LPI-induced signaling. In contrast, upon simultaneous ex-pression of GDE3 and cannabinoid receptor CB2, 2-acyl LPI evoked the same signal as that induced by 2-AG. These data strongly suggest that, in addition to degrading the GPR55 LPI ligand, GDE3 can act as a switch between GPR55 and CB2 signaling. Coincident with a major expression of both GDE3 and CB2 in the spleen, spleens from transgenic mice lacking GDE3 displayed doubling of LPI content compared with WT mice. Decreased production of 2-AG in whole spleen was also observed, supporting the in vivo relevance of our findings. These data thus open a new research avenue in the field of endocannabinoid generation and reinforce the view of GPR55 and LPI being genuine actors of the endocannabinoid system.
Keywords: 2-arachidonoylglycerol; CB1; CB1/CB2; CB2; G-protein–coupled receptor (GPCR); GDPD2); GPR55; endocannabinoid; glycerophosphodiesterase 3 (GDE3; lysophosphatidylinositol; lysophospholipid; monoacylglycerol; phospholipase C.
© 2020 Briand-Mésange et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
From Classical to Alternative Pathways of 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Synthesis: AlterAGs at the Crossroad of Endocannabinoid and Lysophospholipid Signaling.Molecules. 2024 Aug 4;29(15):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153694. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of human glycerophosphodiesterase 3 as an ecto phospholipase C that converts the G protein-coupled receptor 55 agonist lysophosphatidylinositol to bioactive monoacylglycerols in cultured mammalian cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Sep;1865(9):158761. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158761. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32629025
-
The actions and metabolism of lysophosphatidylinositol, an endogenous agonist for GPR55.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013 Dec;107:103-16. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 May 25. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013. PMID: 23714700 Review.
-
Anandamide inhibits FcεRI-dependent degranulation and cytokine synthesis in mast cells through CB2 and GPR55 receptor activation. Possible involvement of CB2-GPR55 heteromers.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Nov;64:298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30243065
-
Brain regional cannabinoid CB(1) receptor signalling and alternative enzymatic pathways for 2-arachidonoylglycerol generation in brain sections of diacylglycerol lipase deficient mice.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014 Jan 23;51:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24012970
Cited by
-
Tiki proteins are glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteases.FEBS Lett. 2022 Apr;596(8):1037-1046. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14320. Epub 2022 Feb 27. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 35182431 Free PMC article.
-
An update on Glycerophosphodiester Phosphodiesterases; From Bacteria to Human.Protein J. 2024 Apr;43(2):187-199. doi: 10.1007/s10930-024-10190-4. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Protein J. 2024. PMID: 38491249 Review.
-
Gene Expression Data Mining Reveals the Involvement of GPR55 and Its Endogenous Ligands in Immune Response, Cancer, and Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 11;22(24):13328. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413328. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948125 Free PMC article.
-
Lipolysis pathways modulate lipid mediator release and endocannabinoid system signaling in dairy cows' adipocytes.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 3;15(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01062-z. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39095900 Free PMC article.
-
What Role Does the Endocannabinoid System Play in the Pathogenesis of Obesity?Nutrients. 2021 Jan 26;13(2):373. doi: 10.3390/nu13020373. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33530406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maccarrone M., Bab I., Bíró T., Cabral G. A., Dey S. K., Di Marzo V., Konje J. C., Kunos G., Mechoulam R., Pacher P., Sharkey K. A., and Zimmer A. (2015) Endocannabinoid signaling at the periphery: 50 years after THC. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 36, 277–296 10.1016/j.tips.2015.02.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

