Incubation with a Complex Orange Essential Oil Leads to Evolved Mutants with Increased Resistance and Tolerance
- PMID: 32916977
- PMCID: PMC7557841
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13090239
Incubation with a Complex Orange Essential Oil Leads to Evolved Mutants with Increased Resistance and Tolerance
Abstract
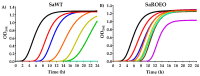
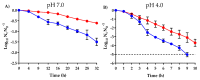
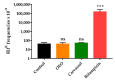
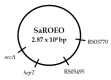
Emergence of strains with increased resistance/tolerance to natural antimicrobials was evidenced after cyclic exposure to carvacrol, citral, and (+)-limonene oxide. However, no previous studies have reported the development of resistance and tolerance to complex essential oils (EOs). This study seeks to evaluate the occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus strains resistant and tolerant to a complex orange essential oil (OEO) after prolonged cyclic treatments at low concentrations. Phenotypic characterization of evolved strains revealed an increase of minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentration for OEO, a better growth fitness in presence of OEO, and an enhanced survival to lethal treatments, compared to wild-type strain. However, no significant differences (p > 0.05) in cross-resistance to antibiotics were observed. Mutations in hepT and accA in evolved strains highlight the important role of oxidative stress in the cell response to OEO, as well as the relevance of the cell membrane in the cell response to these natural antimicrobials. This study demonstrates the emergence of S. aureus strains that are resistant and tolerant to EO (Citrus sinensis). This phenomenon should be taken into account to assure the efficacy of natural antimicrobials in the design of food preservation strategies, in cleaning and disinfection protocols, and in clinical applications against resistant bacteria.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic susceptibility; complex orange essential oil; genotypic resistance; growth kinetics; minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations; mutagenesis frequency; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Variants and Phenotypic Characteristics of Salmonella Typhimurium-Resistant Mutants after Exposure to Carvacrol.Microorganisms. 2020 Jun 22;8(6):937. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060937. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32580471 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-Inhibitory Doses of Individual Constituents of Essential Oils Can Select for Staphylococcus aureus Resistant Mutants.Molecules. 2019 Jan 4;24(1):170. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010170. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30621156 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mutant populations of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e under selective pressure of Thymbra capitata essential oil question its use in food preservation.Food Res Int. 2021 Jul;145:110403. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110403. Epub 2021 May 12. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34112406
-
Emergence of Hyper-Resistant Escherichia coli MG1655 Derivative Strains after Applying Sub-Inhibitory Doses of Individual Constituents of Essential Oils.Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 4;7:273. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00273. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26973641 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium genetic variants isolated after lethal treatment with Thymbra capitata essential oil (TCO) showed increased resistance to TCO in milk.Int J Food Microbiol. 2021 Dec 16;360:109443. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109443. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Int J Food Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34710810
Cited by
-
Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Feb 4;11(2):200. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020200. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic and Genotypic Comparison of Antimicrobial-Resistant Variants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella Typhimurium Isolated from Evolution Assays with Antibiotics or Commercial Products Based on Essential Oils.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;16(10):1443. doi: 10.3390/ph16101443. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895914 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive evolution of Salmonella Typhimurium LT2 exposed to carvacrol lacks a uniform pattern.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;108(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12840-6. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38175235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Espina L., Berdejo D., Alfonso P., García-Gonzalo D., Pagán R. Potential use of carvacrol and citral to inactivate biofilm cells and eliminate biofouling. Food Control. 2017;82:256–265. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.07.007. - DOI
-
- Leite de Souza E. The effects of sublethal doses of essential oils and their constituents on antimicrobial susceptibility and antibiotic resistance among food-related bacteria: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016;56:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2016.07.012. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

