Long-term persistence of anti-HBs after hepatitis B vaccination among isolated anti-HBc positive adults in China: 8-years results
- PMID: 32915691
- PMCID: PMC8018461
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1806672
Long-term persistence of anti-HBs after hepatitis B vaccination among isolated anti-HBc positive adults in China: 8-years results
Abstract
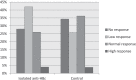
The long-term persistence of hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs) after hepatitis B vaccination among adults harboring isolated hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) is not yet clarified. The present study aimed to assess the immunogenicity and persistence of antibodies in adults 8 years after vaccination. A total of 309 participants including 94 participants in the isolated anti-HBs group and 215 in the control group were recruited in this study. All subjects received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine (20 μg) at 0, 1, and 12 months, followed by testing for serological responses 1 month after the third vaccination. Subsequently, 154 participants were excluded because their anti-HBs data of 8 y after the first vaccination were missing. The prevalence of isolated anti-HBc was about 11.5%, the positive seroprotection rate was 72%, and the geometric mean titer (GMT) value of anti-HBs titer was 24.55 mIU/mL in the isolated anti-HBc group 8 y after three doses of vaccination. No significant difference was detected in the positive seroprotection rate (P = .434) and the GMT values of anti-HBs titers (P = .674) between the isolated anti-HBc and control groups after 8 y. In conclusion, isolated anti-HBc-positive subjects could achieve satisfactory long-term immune effects after hepatitis B vaccination. The GMT values of anti-HBs titers were lower than those of the control group at 1 month, but no significant difference was detected after 8 years.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; isolated anti-HBc; vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Responses to hepatitis B vaccine in isolated anti-HBc positive adults.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Jul 2;12(7):1847-51. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1139256. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27065099 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term persistence of anti-HBs after hepatitis B vaccination among adults: 8-year results.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Mar 3;16(3):687-692. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1666612. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 31526223 Free PMC article.
-
Significance and anamnestic response in isolated hepatitis B core antibody-positive individuals 18 years after neonatal hepatitis B virus vaccination in Taiwan.Vaccine. 2012 Jun 8;30(27):4034-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.04.031. Epub 2012 Apr 22. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 22531558
-
[Anti-HBs persistence following primary vaccination with three doses of hepatitis B vaccine among normal and high-responder adults: a 3-year follow-up study].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;50(6):478-83. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.06.002. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27256725 Chinese.
-
[Anti-HBs persistence following revaccination with three doses of hepatitis B vaccine among low-responsive adults after primary vaccination: a 4-year follow-up study].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;50(6):491-6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.06.004. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27256727 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Overt and occult hepatitis B virus infection detected among chronic kidney disease patients on haemodialysis at a Tertiary Hospital in Ghana.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 4;19(3):e0290917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290917. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38437229 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence of Immunity in Adults after 1, 5 and 10 Years with Recombinant Hepatitis B Vaccine in Beijing in 2010-2020.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jan 25;10(2):181. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020181. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global hepatitis report, 19 April 2017. [OL]. [cited 2020 May 5]. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/global-hepatitis-report-2017.
-
- World Health Organization . Hepatitis B [OL]. 18 July 2019. [cited 2020 May 5]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b.
-
- Wang FZ, Zheng W, Su XJ, Miao N, Zhang GM, Yin ZD.. Achievements and prospects for hepatitis B prevention and control in China. Chin J Vacc Immun. 2019;25:487–92. (In Chinese).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical