Phase I Study of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Alone or With Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma and Other Genitourinary Tumors
- PMID: 32915679
- PMCID: PMC7605393
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.01652
Phase I Study of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Alone or With Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma and Other Genitourinary Tumors
Abstract
Purpose: We assessed the safety and efficacy of cabozantinib and nivolumab (CaboNivo) and CaboNivo plus ipilimumab (CaboNivoIpi) in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC) and other genitourinary (GU) malignances.
Patients and methods: Patients received escalating doses of CaboNivo or CaboNivoIpi. The primary objective was to establish a recommended phase II dose (RP2D). Secondary objectives included objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), duration of response (DoR), and overall survival (OS).
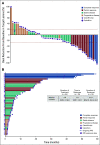
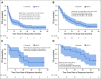
Results: Fifty-four patients were enrolled at eight dose levels with a median follow-up time of 44.6 months; data cutoff was January 20, 2020. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) occurred in 75% and 87% of patients treated with CaboNivo and CaboNivoIpi, respectively, and included fatigue (17% and 10%, respectively), diarrhea (4% and 7%, respectively), and hypertension (21% and 10%, respectively); grade 3 or 4 immune-related AEs included hepatitis (0% and 13%, respectively) and colitis (0% and 7%, respectively). The RP2D was cabozantinib 40 mg/d plus nivolumab 3 mg/kg for CaboNivo and cabozantinib 40 mg/d, nivolumab 3 mg/kg, and ipilimumab 1 mg/kg for CaboNivoIpi. ORR was 30.6% (95% CI, 20.0% to 47.5%) for all patients and 38.5% (95% CI, 13.9% to 68.4%) for patients with mUC. Median DoR was 21.0 months (95% CI, 5.4 to 24.1 months) for all patients and not reached for patients with mUC. Median PFS was 5.1 months (95% CI, 3.5 to 6.9 months) for all patients and 12.8 months (95% CI, 1.8 to 24.1 months) for patients with mUC. Median OS was 12.6 months (95% CI, 6.9 to 18.8 months) for all patients and 25.4 months (95% CI, 5.7 to 41.6 months) for patients with mUC.
Conclusion: CaboNivo and CaboNivoIpi demonstrated manageable toxicities with durable responses and encouraging survival in patients with mUC and other GU tumors. Multiple phase II and III trials are ongoing for these combinations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02496208.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Final Results From a Phase I Trial and Expansion Cohorts of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Alone or With Ipilimumab for Advanced/Metastatic Genitourinary Tumors.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 1;42(25):3033-3046. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02233. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38954785 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab Phase I Expansion Study in Patients with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Refractory to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 1;28(7):1353-1362. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3726. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35031545 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):1370-1385. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30413-9. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31427204 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Management of adverse events associated with cabozantinib plus nivolumab in renal cell carcinoma: A review.Cancer Treat Rev. 2022 Feb;103:102333. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102333. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022. PMID: 35033866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of cabozantinib for malignant tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024 May;24(5):293-302. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2024.2337266. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38551185 Review.
Cited by
-
Cabozantinib Plus Nivolumab in Adult Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective, Non-Interventional Study in a Real-World Cohort/GUARDIANS Project.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;16(17):2998. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172998. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272856 Free PMC article.
-
Camrelizumab combined with anlotinib as second-line therapy for metastatic or recurrent small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 8;14:1391828. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1391828. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39040456 Free PMC article.
-
Final Results From a Phase I Trial and Expansion Cohorts of Cabozantinib and Nivolumab Alone or With Ipilimumab for Advanced/Metastatic Genitourinary Tumors.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 1;42(25):3033-3046. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02233. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38954785 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
New Therapeutic Horizons for Advanced or Metastatic Penile Cancer.Urol Clin North Am. 2024 Aug;51(3):367-376. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2024.03.005. Epub 2024 May 18. Urol Clin North Am. 2024. PMID: 38925739 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Precision: A Narrative Review Exploring the Critical Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 17;25(10):5490. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105490. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7-30, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Sharma P Retz M Siefker-Radtke A, et al. : Nivolumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum therapy (CheckMate 275): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:312-322, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

