Protein N-Terminal Acetylation: Structural Basis, Mechanism, Versatility, and Regulation
- PMID: 32912665
- PMCID: PMC7749037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.08.005
Protein N-Terminal Acetylation: Structural Basis, Mechanism, Versatility, and Regulation
Abstract
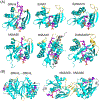
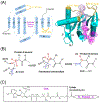
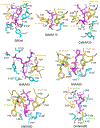
N-terminal acetylation (NTA) is one of the most widespread protein modifications, which occurs on most eukaryotic proteins, but is significantly less common on bacterial and archaea proteins. This modification is carried out by a family of enzymes called N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). To date, 12 NATs have been identified, harboring different composition, substrate specificity, and in some cases, modes of regulation. Recent structural and biochemical analysis of NAT proteins allows for a comparison of their molecular mechanisms and modes of regulation, which are described here. Although sharing an evolutionarily conserved fold and related catalytic mechanism, each catalytic subunit uses unique elements to mediate substrate-specific activity, and use NAT-type specific auxiliary and regulatory subunits, for their cellular functions.
Keywords: HYPK; IP(6); N-terminal acetylation; NATs; co-translational modification; enzyme mechanism; post-translational modification; ribosome.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Probing the interaction between NatA and the ribosome for co-translational protein acetylation.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 10;12(10):e0186278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186278. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29016658 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and mechanism of non-histone protein acetyltransferase enzymes.FEBS J. 2013 Nov;280(22):5570-81. doi: 10.1111/febs.12373. Epub 2013 Jun 28. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23742047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteome-derived peptide libraries allow detailed analysis of the substrate specificities of N(alpha)-acetyltransferases and point to hNaa10p as the post-translational actin N(alpha)-acetyltransferase.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 May;10(5):M110.004580. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.004580. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21383206 Free PMC article.
-
Co-translational, Post-translational, and Non-catalytic Roles of N-Terminal Acetyltransferases.Mol Cell. 2019 Mar 21;73(6):1097-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.007. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30878283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using cell lysates to assess N-terminal acetyltransferase activity and impairment.Methods Enzymol. 2023;686:29-43. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2023.02.024. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Methods Enzymol. 2023. PMID: 37532404
Cited by
-
Influenza A Virus and Acetylation: The Picture Is Becoming Clearer.Viruses. 2024 Jan 17;16(1):131. doi: 10.3390/v16010131. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38257831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structurally Modified Bioactive Peptide Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Lentiviral Particles Expression.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 26;14(10):2045. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102045. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297481 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Roles of ISG15/ISGylation in Cancer.Molecules. 2023 Jan 31;28(3):1337. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031337. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-terminal α-amino SUMOylation of cofilin-1 is critical for its regulation of actin depolymerization.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 14;14(1):5688. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41520-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37709794 Free PMC article.
-
Extended N-Terminal Acetyltransferase Naa50 in Filamentous Fungi Adds to Naa50 Diversity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10805. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810805. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohamed AE and Mohamed AR (2018) Post-translational N-terminal Arginylation of Protein Fragments: A Pivotal Portal to Proteolysis. Current Protein & Peptide Science 19, 1214–1223 - PubMed
-
- Giglione C, et al. (2015) N-terminal protein modifications: Bringing back into play the ribosome. Biochimie 114, 134–146 - PubMed
-
- Aksnes H, et al. (2016) First Things First: Vital Protein Marks by N-Terminal Acetyltransferases. Trends Biochem Sci 41, 746–760 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

