Impact of Bone Marrow miR-21 Expression on Acute Myeloid Leukemia T Lymphocyte Fragility and Dysfunction
- PMID: 32911844
- PMCID: PMC7563595
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9092053
Impact of Bone Marrow miR-21 Expression on Acute Myeloid Leukemia T Lymphocyte Fragility and Dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a hematopoietic malignancy in which antitumor immunity is impaired. The therapeutic management of AML requires understanding the mechanisms involved in the fragility and immune dysfunction of AML T lymphocytes.
Methods: In this study, T lymphocytes from healthy donors (HD) and AML patients were used. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) from leukemic cells were screened for their microRNA content and impact on T lymphocytes. Flow cytometry, transcriptomic as well as lentiviral transduction techniques were used to carry out the research.
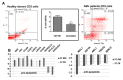
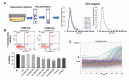
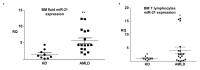
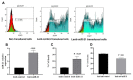
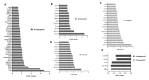
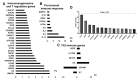
Results: We observed increased cell death of T lymphocytes from AML patients. EVs from leukemia myeloid cell lines harbored several miRNAs, including miR-21, and were able to induce T lymphocyte death. Compared to that in HD, miR-21 was overexpressed in both the bone marrow fluid and infiltrating T lymphocytes of AML patients. MiR-21 induces T lymphocyte cell death by upregulating proapoptotic gene expression. It also increases the immunosuppressive profile of T lymphocytes by upregulating the IL13, IL4, IL10, and FoxP3 genes.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that miR-21 plays a significant role in AML T lymphocyte dysfunction and apoptosis. Targeting miR-21 may be a novel approach to restore the efficacy of the immune response against AML.
Keywords: AML; T lymphocytes; apoptosis; extracellular vesicles; immunosuppression; miR21.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. They confirm that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this publication. The manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High bone marrow miR-19b level predicts poor prognosis and disease recurrence in de novo acute myeloid leukemia.Gene. 2018 Jan 15;640:79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.034. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29032147
-
MiR-100 regulates cell viability and apoptosis by targeting ATM in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Feb 19;522(4):855-861. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.156. Epub 2019 Dec 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 31801665
-
LncRNA ANRIL promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion during acute myeloid leukemia pathogenesis via negatively regulating miR-34a.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020 Feb;119:105666. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105666. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31830533
-
EV-mediated intercellular communication in acute myeloid leukemia: Transport of genetic materials in the bone marrow microenvironment.Exp Hematol. 2024 May;133:104175. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2024.104175. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Exp Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38311165 Review.
-
Role of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)-Derived exosomes in tumor progression and survival.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jun;150:113009. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113009. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35486974 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential role of serum extracellular vesicle derived small RNAs in AML research as non-invasive biomarker.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Feb 20;5(6):1691-1705. doi: 10.1039/d2na00959e. eCollection 2023 Mar 14. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 36926576 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Leukemia-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Elicit Antitumor Immune Response.J Blood Med. 2021 May 17;12:277-285. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S308861. eCollection 2021. J Blood Med. 2021. PMID: 34040472 Free PMC article.
-
Acute myeloid leukemia-derived exosomes deliver miR-24-3p to hinder the T-cell immune response through DENN/MADD targeting in the NF-κB signaling pathways.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 21;21(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01259-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37735672 Free PMC article.
-
ActivinA modulates B-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell communication and survival by inducing extracellular vesicles production.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 12;14(1):16083. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66779-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38992199 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells obstruct AML-targeting CD8+ clonal effector and CAR T-cell function while promoting a senescence-associated phenotype.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Jan 17;73(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03594-1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38231344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dohner H., Estey E., Grimwade D., Amadori S., Appelbaum F.R., Buchner T., Dombret H., Ebert B.L., Fenaux P., Larson R.A., et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:424–447. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

